Plants are found all over the Earth. They are found on land, in freshwater, and in the ocean. Plants have the following three features that distinguish them from other living organisms:
- Plants have chlorophyll, a green pigment necessary for photosynthesis.
- Their cell walls are made sturdy by a material called cellulose.
- They are fixed in one place (they don't move).
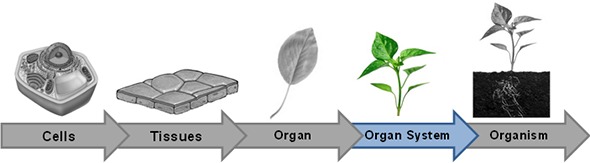
Plants have two organ systems, the shoot system and the root system. The shoot system is above the ground. The shoot system includes organs such as leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits. The root system is below the ground. The root system includes the roots and modified stem structures such as rhizomes and tubers.
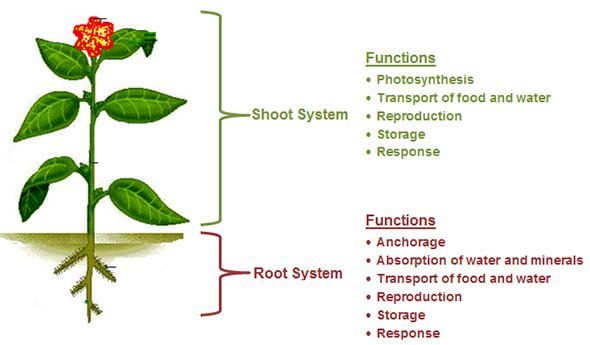
Each plant system has specialized functions. The graphic below identifies the function of the shoot and root systems of plants.
There are four types of organs found in plants: roots, stems, leaves, and reproductive structures. The image below shows the main functions of plant organs.
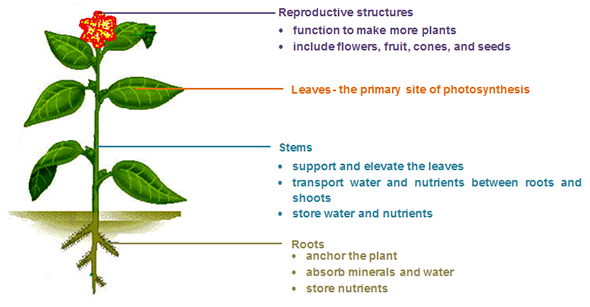
Not all plants have all of these organs, and some plants have modified versions of these organs. For example, cacti have modified leaves called spines, and potatoes are modified stems called tubers.
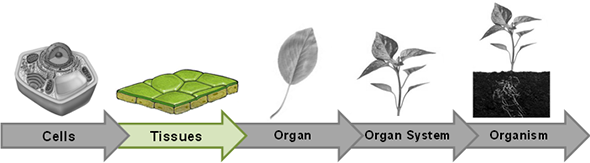
Plants have three types of tissue: dermal, vascular, and ground tissue. These three tissues can be found throughout the plant.
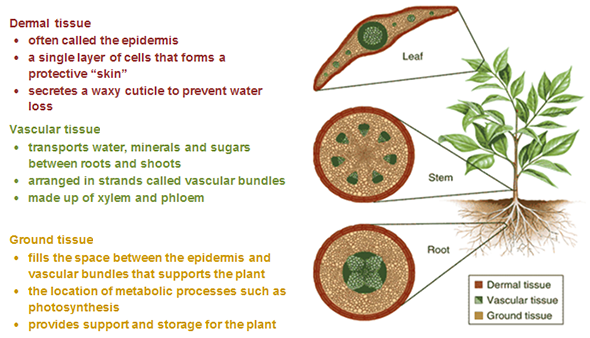
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that have a cell wall and chloroplasts. As plant cells grow and mature, they become specialized to do specific jobs within the plant. For example, guard cells are located in the epidermis of leaves and control the opening and closing of the stomata. Phloem cells are found in the vascular tissue and carry nutrients throughout the plant. Xylem cells are also found in the vascular tissue and carry water throughout the plant.