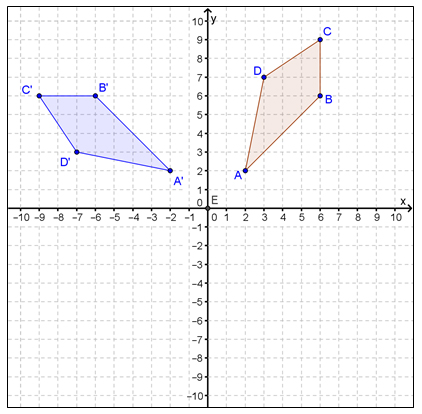
In the figure below, quadrilateral ABCD is rotated 90° counterclockwise about the origin to generate quadrilateral A'B'C'D'.

Which of the following best describes the algebraic rule for this transformation?
A. (x, y) → (-y, x)
Correct!
B. (x, y) → (-x, y)
Incorrect. How do the coordinates of point D change in order to become the coordinates of point D'?
C. (x, y) → (y, x)
Incorrect. How do the coordinates of point D change in order to become the coordinates of point D'?
D. (x, y) → (-y, -x)
Incorrect. How do the coordinates of point D change in order to become the coordinates of point D'?
Which of the following properties about geometric transformations are true?
A. I and II only
Incorrect. A dilation changes the length of a polygon’s side by a given scale factor. However, the orientation of the polygon remains the same.
B. II and III only
Incorrect. A rotated figure has the same size and shape as the preimage, and a dilated figure has a different size, but the same shape as the preimage.
C. I and III only
Incorrect. Both translations and reflections are congruence transformations, so they preserve a polygon’s side length.
D. I, II, and III
Correct!
Which of the following is not a congruence transformation?
A. (x, y) → (x − 3, y + 5)
Incorrect. This transformation represents a translation, which is a congruence transformation. All points on the figure are translated 3 units to the left and 5 units up, but the size and shape of the figure is preserved.
B. (x, y) → (2.5x, 2.5y )
Correct!
C. (x, y) → (x, -y)
Incorrect. This transformation represents a reflection across the x-axis, which is a congruence transformation. All points on the figure are reflected, but the size and shape of the figure is preserved.
D. (x, y) → (-y, x)
Incorrect. This transformation represents a 90° counterclockwise rotation about the origin, which is a congruence transformation. All points on the figure are rotated, but the size and shape of the figure is preserved.
Pentagon ABCDE is transformed into the figures that are shown below.
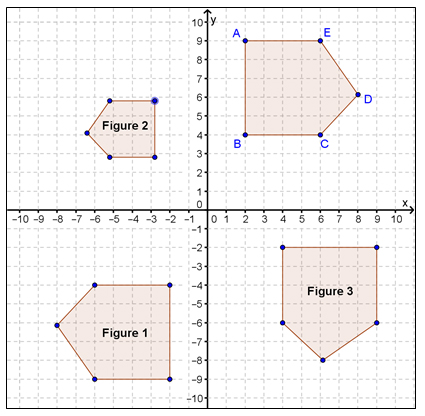
Which of the figures represents a congruence transformation?
A. Figure 1 only
Incorrect. Figure 1 is a rotation of ABCDE, which is a congruence transformation. However, so is Figure 3.
B. Figure 1 and Figure 2 only
Incorrect. Figure 1 is a rotation of ABCDE, which is a congruence transformation. However, Figure 2 is a dilation of ABCDE, which is not a congruence transformation.
C. Figure 1 and Figure 3 only
Correct!
D. Figure 2 only
Incorrect. Figure 2 is a dilation of ABCDE, which is not a congruence transformation. Look closely at Figures 1 and 3.
In the figure below, parallelogram ABCD was rotated 90° counterclockwise about the origin to generate parallelogram A'B'C'D'.
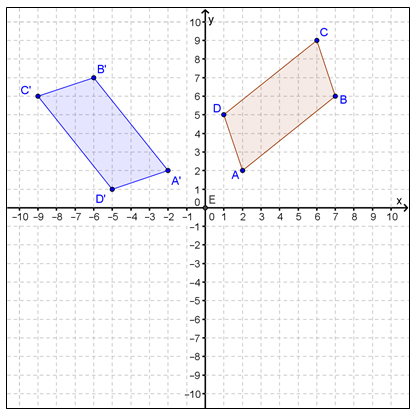
Which of the following transformations would not have resulted in AB ≅ A'B'?
A. (x, y) → (x, -y)
Incorrect. This mapping represents a reflection across the x-axis, which is a congruence transformation, and preserves the side length of the preimage to generate the image.
B. (x, y) → (x − 1, y – 4)
Incorrect. This mapping represents a translation, which is a congruence transformation, and preserves the side length of the preimage to generate the image.
C. (x, y) → (1.5y, 1.5x)
Correct!
D. (x, y) → (-y, x)
Incorrect. This mapping represents a rotation, which is a congruence transformation, and preserves the side length of the preimage to generate the image.