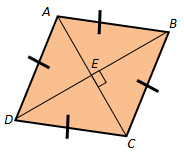
If a parallelogram is a rhombus, the diagonals bisect the opposite angles.
In rhombus ABCD, m∠BAE = 4x + 15 and m∠DAE = 2x + 29.
Find m∠BAE, m∠DAE, and m∠BAD.

First, set up an equation. Since ABCD is a rhombus, we know that diagonal AC bisects ∠BAD. This means that ∠BAE ≅ ∠DAE:
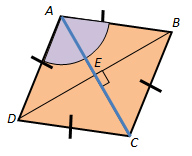
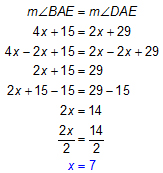
Now, substitute the value of x into the expression for each angle measure.

Close this tab or window to return to the lesson.