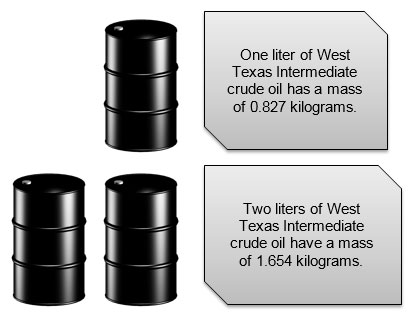
In mathematics, you will frequently work with relationships among different quantities. A variable is used to represent these quantities. For example, consider the relationship between the mass of a substance and the volume of a substance.

The relationship between the mass of crude oil and the volume of crude oil is called a multiplicative relationship. For each barrel of crude oil, if you know the volume, V, in liters, you can calculate the mass, m, of the crude oil in kilograms by multiplying the volume by 0.827.
Oil is typically sold by volume, so in the relationship between mass and volume, volume is the independent variable, or the input variable that is used to make a calculation. Because the mass of the oil depends on the volume, mass is the dependent variable.
Another type of relationship is an additive relationship. An empty metal barrel of oil weighs about 40 pounds. One gallon of crude oil weighs 7.2 pounds.
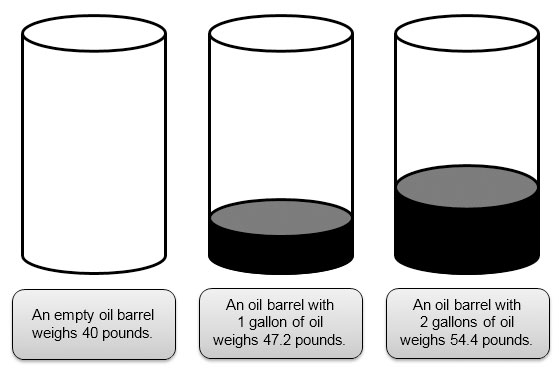
In this lesson, you will use verbal descriptions, tables, graphs, and equations to represent both multiplicative and additive relationships. You will also use tables of data to write equations that relate the independent variable and the dependent variable.