Source: Strong and weak electrolytes, Conquering Chemistry, http://www.cci.net.au/conqchem/PCmod3text06.htm
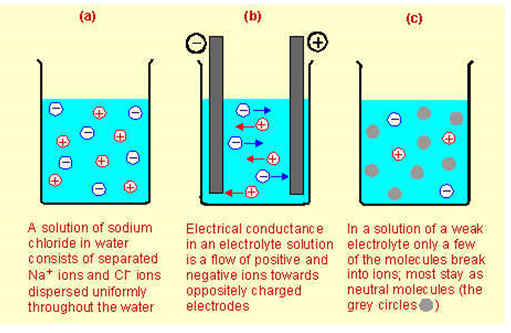
Compounds that conduct electricity in solution or when molten because their ions are free to move around are called electrolytes. In solution (or molten), ions separate from each other and move independently throughout the solution.
Strong electrolytes are substances that only exist as ions in solution. Ionic compounds are typically strong electrolytes. Strong acids, strong bases and salts are strong electrolytes. When solid NaCl is placed in water, it completely dissociates to form Na+ and Cl- ions.
A weak electrolyte only partially dissociates in solution and produces relatively few ions. Polar covalent compounds are typically weak electrolytes. Weak acids and weak bases are weak electrolytes.A nonelectrolyte does not dissociate at all in solution and therefore does not produce any ions. Nonelectrolytes are typically polar covalent substances that do dissolve in water as molecules instead of ions. Sugar (C12H22O11) is a good example of a nonelectrolyte.
