

Think about the rate that sugar dissolves in hot tea verses cold tea. Many people do not like to add sugar to ice tea because it does not taste the same. Why would sugar not dissolve well in cold tea? Let’s investigate!
![]() Click on the beaker to begin the activity.
Click on the beaker to begin the activity.
Conclusion: Describe in your notes the difference in the rate of dissolving the sugar in the hot and cold water. Then use this evidence to generalize the effect of temperature on the rate of dissolving solids.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The sugar dissolved about 10 seconds faster in the hot water than in the cold water. Solids appear to dissolve faster when the temperature of the solution is increased.
Remember that temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules. The higher the temperature, the faster the molecules are moving. Solids dissolve faster at higher temperatures because the molecules are moving more quickly; therefore, solvent molecules are able to surround solute molecules more quickly.
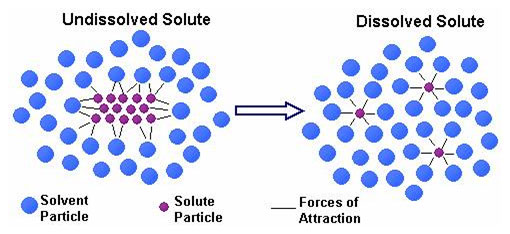
In the investigation above, both solutions are stirred. Another word for stirring is agitation. Look at the diagram above that represents the dissolving process. In your notes, explain why stirring would increase the rate of dissolving.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Agitation increases the rate that the solute and solvent molecules collide. Solute and solvent molecules must collide for dissolving to happen.
Sometimes, sugar cubes are used instead of granulated sugar. Granulated sugar dissolves faster than sugar cubes.

Which piece of equipment could be used to increase the surface area of the sugar cubes to increase the rate of dissolving? Click on the pieces of equipment to check your answers.
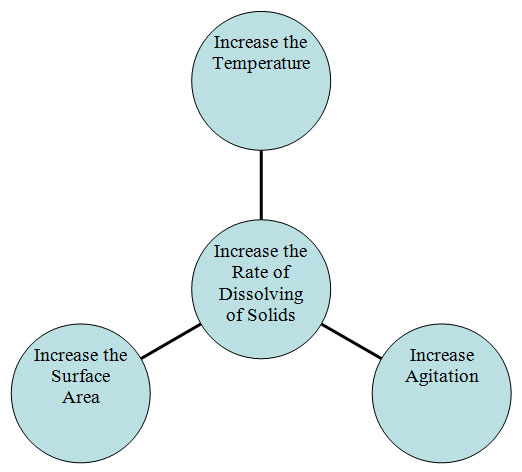
In summary, the three factors that influence the rate at which solids dissolve in liquids are temperature, agitation, and surface area. The concept map below shows this summary.
Sources for images used in this section, as they appear, from top to bottom: