
One of the ways that the nucleus can make itself stable is to change a neutron to a proton. This is a complex process, but the final product is a stable nucleus and an extra electron that comes racing out of the nucleus with a really high energy. This high-energy electron gets a special name—it's called a beta particle. The nucleus also emits a very tiny sub atomic particle called an antineutrino.

When a substance undergoes beta radiation it gives off beta particles. A beta particle has a negative charge and such small mass we can assume it to be zero.
A beta particle can be written three ways:
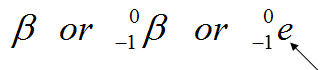
We use an e because a beta particle is simply a fast moving electron.
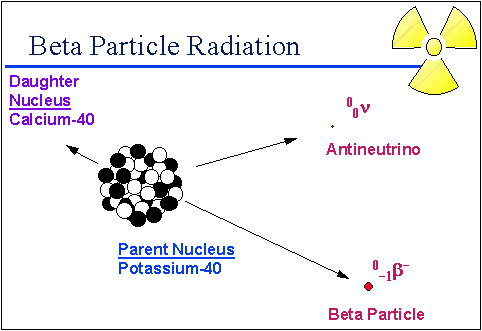
Source: Beta Radiation, University of Michigan Student Chapter of the Health Physics Society
A beta particle is essentially an electron that is spontaneously emitted from the nucleus of an unstable atom. Here are some examples of beta emitters:
Beta particles are less massive than alpha particles. They have a charge of -1 (electron). They can also travel farther and through more substances than alpha particles. Some beta particles with high energies, like those emitted from P-32, can penetrate the skin. Others, such as those emitted from tritium (H-3) cannot penetrate the outer skin layer. Metal and plastic can stop beta particles.
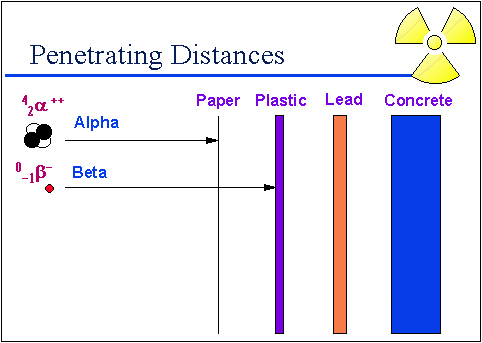
Source: Penetrating distances, University of Michigan Student Chapter of the Health Physics Society
Many beta emitters can be dangerous if you inhale, ingest, or absorb them into the body (but a banana is still safe).
Watch beta decay occur for a collection of nuclei or for an individual nucleus.

Now answer the following questions.
You can also watch the carbon-14 isotope decay by clicking on the C-14 nucleus below the He-3 nucleus.