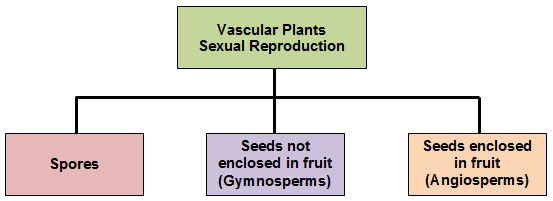
Sexual reproduction in plants involves the joining together of gametes (the sperm and the egg). This joining results in the mixing of genetic material. Vascular plants can reproduce sexually by means of spores or seeds.

Seedless vascular plants, such as ferns, reproduce through spores. The life cycle of ferns is an example of alternation of generations. During the fern’s life cycle, there is an alternation of a sexual phase, the gametophyte, and a nonsexual phase, the sporophyte.
![]() The image below shows the life cycle of a fern. Click on each number to learn more about the various stages in the life cycle of a fern.
The image below shows the life cycle of a fern. Click on each number to learn more about the various stages in the life cycle of a fern.
The word gymnosperm means “naked seed.” A gymnosperm is a vascular plant that has seeds that are not protected by an ovary or fruit. Conifers, such as pine trees are examples of gymnosperms. The image below shows the life cycle of a conifer. The life cycle of a conifer is also an example of alternation of generations.
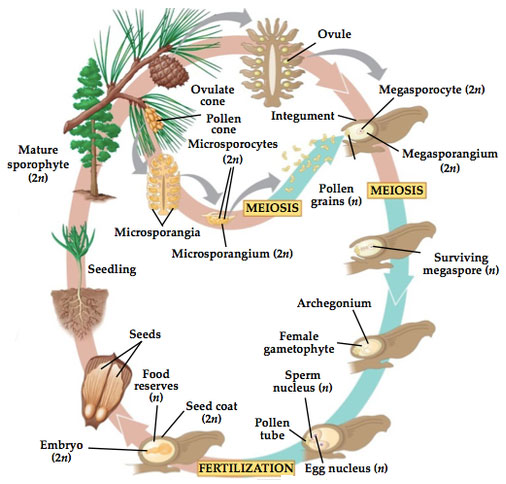
![]() Watch this video to learn about what happens during the life cycle of a conifer.
Watch this video to learn about what happens during the life cycle of a conifer.
Source: Gymnosperm Reproduction, Educreations, YouTube
Sources for images used in this section, as they appear, top to bottom: