Let's continue learning where variations in populations come from.
Nonrandom mating is the process of individuals choosing a mate based on a certain characteristic. Birds are a primary example of this.
![]() Watch the video below about the peacock species for further explanation.
Watch the video below about the peacock species for further explanation.
Source: Natural Selection: Tale of the Peacock, Acorvettes, YouTube
Genetic drift is the change in the frequency of an allele due to random changes as opposed to natural selection. Genetic drift occurs in small, reproductively isolated populations. Genetic drift has minimal effects on large populations. The effect of chance events lead to the following:
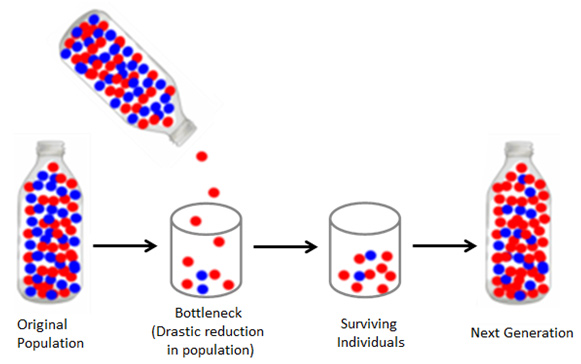
Source: Adapted from: Bottleneck effect 3, Martha Lee, Clikr
Describe how this image represents the bottleneck effect in your notes.
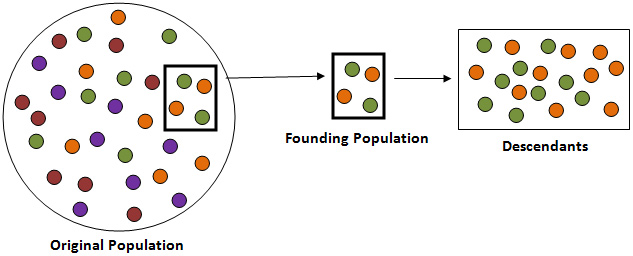
Describe how this image represents the founder effect in your notes.
Natural selection results in different survival and reproduction rates due to changing environmental conditions. This can result from climate change, food source availability, predators, parasites, diseases, or toxins. The combinations of alleles that provide "fitness" increase in the population. This is an adaptive evolutionary change.
![]() Watch the following video to see how the process of natural selection operates in populations of rainforest hummingbirds.
Watch the following video to see how the process of natural selection operates in populations of rainforest hummingbirds.
Source: Evolution Primer #4: How does Evolution Really Work?,Gravitationalist, YouTube