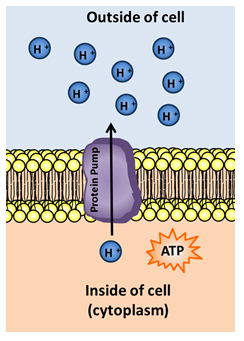
Active transport is the movement of a substance across a cell membrane with the input of energy (ATP). During active transport, proteins move substances against a concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration, generally with the help of transfer proteins, thus requiring energy.

![]() Watch the following video on the Sodium Potassium Pump which is an example of active transport.
Watch the following video on the Sodium Potassium Pump which is an example of active transport.
Source: Active Transport, micrbett, YouTube
Sometimes, the cell needs to move large molecules into and out of the cell. When these molecules are too big to pass through the plasma membrane, the cell utilizes the process of endocytosis and exocytosis.
|
|
![]() Watch this video on endocytosis and exocytosis.
Watch this video on endocytosis and exocytosis.
Source: Endocytosis and Exocytosis, cecamgmacz, YouTube