Source: Starchy Foods, US Department of Agriculture, Wikimedia Commons

Source: Starchy Foods, US Department of Agriculture, Wikimedia Commons
When you hear the word carbohydrate, you probably think of grain products such as the ones pictured to the right. Let’s break the word carbohydrate down and analyze the parts.
Carbo, refers to carbon and hydra, comes from the word water. So, you can think of carbohydrates as carbon plus water. Carbohydrates are compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. In carbohydrates, the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are usually found in the ration of 1:2:1. Carbohydrates have the general chemical formula of CH2O.
There are two main classes of carbohydrates: simple sugars and complex carbohydrates.
The monomer of a carbohydrate is a monosaccharide. Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Notice that each of these end in the Latin suffix –ose. The suffix means “full of” and is used in chemistry when naming sugars. The structures of glucose, fructose, and galactose are shown below. Under each structure is the chemical formula of the compound.
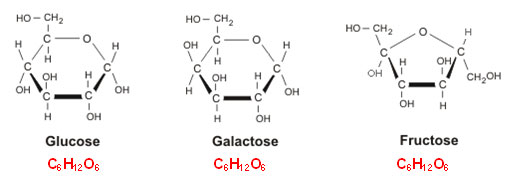
Source: Glucose, galactose and fructose, Food Science and Technology
If you look closely at the molecular formulas, you will notice they are all the same. Glucose, fructose, and galactose are what chemists refer to as isomers. Isomers have the same chemical formula, but the atoms in the molecule are attached differently.
You know that glucose is a product of photosynthesis. Glucose is often referred to as blood sugar because it is the immediate source of energy during cellular respiration. All carbohydrates are broken down into glucose for transport via the bloodstream and used by the cells of the body. Galactose is the sugar in milk and yogurt while fructose is a sugar commonly found in fruit.

Source: Bag of Sugar, Domino Sugar
What about table sugar? What type of sugar is it?
Table sugar, or sucrose, is a disaccharide. In chemistry, the prefix di– means two. A disaccharide is a polymer that is made up of two monosaccharaides.
Specifically, sucrose is made up of a glucose and fructose molecule bonded together. Remember, the process that joins monomers together to make polymers is called dehydration synthesis.
![]() Click on the button that says bond to see a glucose and fructose molecule join together to make a sucrose molecule.
Click on the button that says bond to see a glucose and fructose molecule join together to make a sucrose molecule.
The process of hydrolysis, which happens during cellular respiration, is the reverse of dehydration synthesis. Hydrolysis is the process of breaking compounds into smaller molecules by adding water.
![]() Click on the add water button to see an animation of hydrolysis.
Click on the add water button to see an animation of hydrolysis.
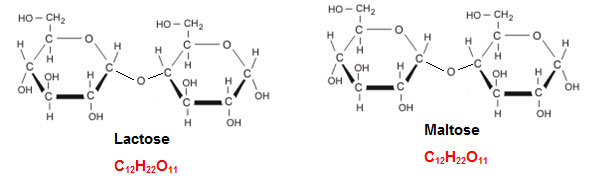
Other common disaccharides are lactose and maltose. Lactose is the major sugar in milk and is made up on the monosaccharide’s glucose and galactose. Maltose is made up of two glucose molecules. The structure of lactose and maltose are shown below.