Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Linear functions have a constant term, which can be a fixed fee, and a rate of change, or slope. In this situation, what is the fixed fee, and what is the rate charged per ticket?
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
35.50x + 12 ≤ 438
 online graphing calculator, or a graphing calculator app to generate a table of values for the equation Y1 = 35.50x + 12 and the equation Y2 = 438. Copy the table below into your notes and use the information from your graphing calculator to complete the table.
online graphing calculator, or a graphing calculator app to generate a table of values for the equation Y1 = 35.50x + 12 and the equation Y2 = 438. Copy the table below into your notes and use the information from your graphing calculator to complete the table.x |
Y1= 35.50x + 12 |
Y2 = 438 |
8 |
||
9 |
||
10 |
||
11 |
||
12 |
||
13 |
||
14 |
You can use an online graphing calculator such as  meta-calculator.
meta-calculator.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
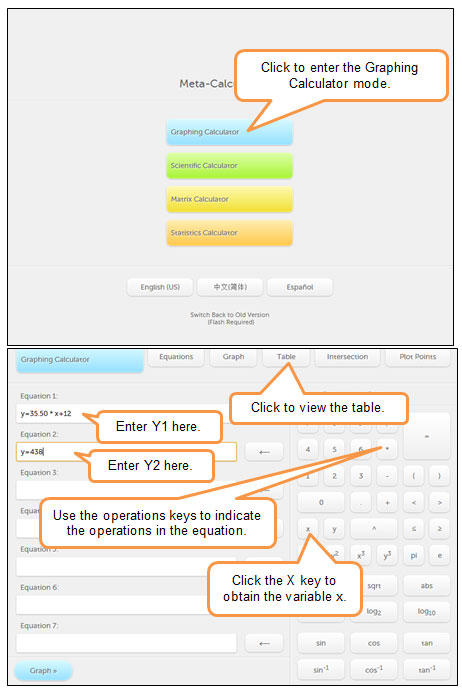
 to see instructions on how to use this online calculator to generate a table of values.
to see instructions on how to use this online calculator to generate a table of values.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
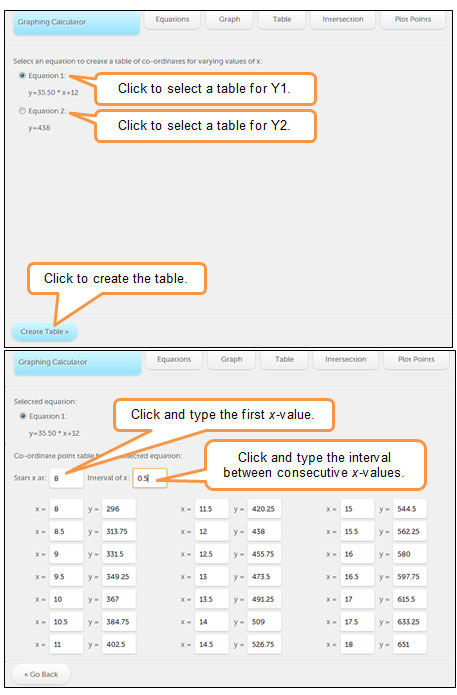
x |
Y1 = 35.50x + 12 |
Y2 = 438 |
8 |
296 |
438 |
9 |
331.5 |
438 |
10 |
367 |
438 |
11 |
402.5 |
438 |
12 |
438 |
438 |
13 |
473.5 |
438 |
14 |
509 |
438 |

Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Read down the Y1 and Y2 columns until you see the same number side by side. Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
x = 12
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
x = 12
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Read the chart upward from x = 12. Would you say that Y1 is less than Y2 or greater than Y2? Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Y1 < Y2
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Y1 < Y2
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Read the chart downward from x = 12. Would you say that Y1 is less than Y2 or greater than Y2? Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Y1 > Y2
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Y1 > Y2
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Read the chart to identify the x-values where Y1 = Y2 and Y1 < Y2? Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
x ≤ 12
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
x ≤ 12
Pause and Reflect
How would the possible values for x change if the budget for the Spanish Club had been $367 instead of $438?
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required. The Spanish Club could have spent no more than $367, so change Y2 to 367 and look for the x-values where Y1 ≤ Y2. We can see that x ≤ 10.
How would your solution strategy be different if the Spanish Club decided to spend at least $400 on concert tickets?
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required. If the situation were "at least $400," then the inequality would be greater than or equal to $400. Instead of looking for x-values where Y1 ≤ Y2, look for x-values where Y1 ≥ Y2.
Practice
- Juliette used a table of values to solve the inequality 4(x – 10) > 8. She entered Y1 = 4(x – 10) and Y2 = 8 into her graphing calculator to generate the table below.
xY1Y29-48100811481288131281416815208Based on the table, what would the solution be to the inequality, 4(x – 10) > 8? Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Determine the x-values where Y1 > Y2, but Y1 ≠ Y2.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
x > 12
- Antoine used a table of values to solve the inequality 4.3(2x + 1.4) < 49.02. He placed Y1 = 4.3(2x + 1.4) into his graphing calculator and obtained the table of values shown below.
Based on the table, what would be the solution to the inequality 4.3(2x + 1.4) < 49.02?xY1331.82440.42549.02657.62766.22874.82
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Determine the x-values where Y1 < 49.02, but Y1 ≠ 49.02. Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
x < 5
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
x < 5
-
Celsa used a table of values to solve the inequality 2x + 3.5 ≥ 3(x – 17). She entered Y1 = 2x + 3.5 and Y2 = 3(x – 17) into her graphing calculator to generate the table below.
xY1Y253109.510853.5110.5109.554111.511154.5112.5112.555113.511455.5114.5115.556115.5117
Based on the table, what would the solution be to the inequality 2x + 3.5 ≥ 3(x – 17)?
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Determine the x-values where Y1 ≥ Y2. Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
x ≥ 54.5
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
x ≥ 54.5