When Conjunctions Connect Subjects

Source: Outdoor Grammar Décor, Adrienne Breaux, Apartment Therepy: Austin
Ensuring that verbs agree in number with their single noun subjects is one thing, but how do you edit for subject-verb agreement when sentences have two or more subjects connected by conjunctions? Two rules will help to answer this question.
Rule #1: Use a plural verb with two or more subjects connected by the conjunction and.

This principle applies only to the use of and, not to the use of phrases such as together with, as well as, or along with because they are not conjunctions.

Exception to the and rule: Use a singular verb when the nouns connected by and are so closely associated with each other that they are considered to be describing one thing.
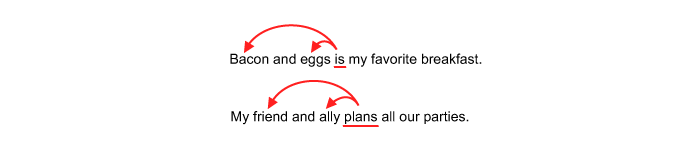
Rule #2: Use a singular verb when singular subjects are connected by the conjunctions or or nor.

When connecting a singular subject and a plural subject with the conjunctions or or nor, be sure the verb agrees in number with the subject that is closer to the verb. Proximity to the verb counts, whether the subject is before the verb or not.

To avoid awkward-sounding sentences like Either my speakers or my printer is broken, some grammar experts suggest that when joining a singular subject and a plural subject with or or nor, put the plural subject closer to the verb, thus requiring a plural verb. That’s just a suggestion, however, and is not mandatory.
In the sentences that follow, practice recognizing subject-verb agreement by choosing “Yes” if they agree in number and "No" if they don’t agree.