

The image above is that of Machu Picchu, an ancient fortress of the Incan civilization, carved into the Andes Mountains of Peru. Recently designated as one of the Seven New Wonders of the World, the intricate architecture of Machu Picchu is an example of the advanced nature in the Incan civilization.
Click on the link below to watch a video about Machu Picchu. Answer the questions that follow in your notes.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The Incas initially abandoned Machu Picchu because of a civil war.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The Incas burned the forest so that it would grow back and cover Machu Picchu, hiding it from the invading Spanish conquistadors.
The Incas ruled an empire that extended along the western coast of Peru. What started as a small civilization in Cuzco around AD 1300 became an empire of nearly 12 million people at the height of its existence. By controlling such a vast area, the Incas gained access to some of the most valuable natural resources in the world. Gold, silver, and copper were located in this region, making the Incas a rich and powerful civilization.
Click the link below to locate the Incan Empire on the map.
According to the map, the Incan Empire was located in which present-day South American countries?
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The Inca Empire was located in present-day Ecuador, Peru, and Chile.
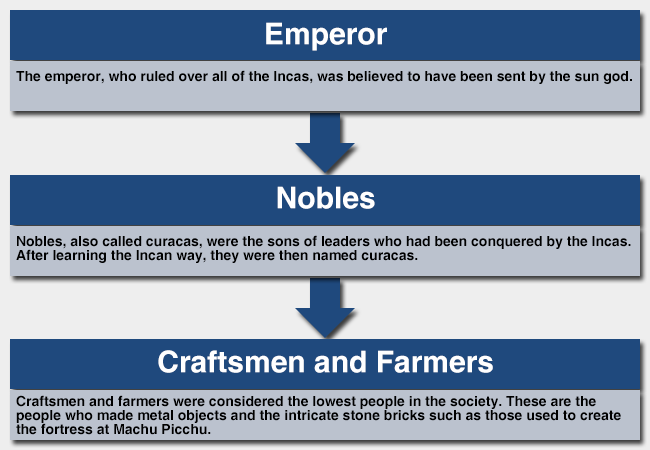
The Incas had a highly structured society. They also had an orderly system of government in which people paid taxes. Some citizens paid in silver and gold while others paid with the yield from their crops. Read the information below about the societal hierarchy.
The Incan Empire is known for its progressive agricultural practices and engineering feats. Although the Incas were located in the mountains, they found ways to grow crops and irrigate them properly. First, they created a complex highway system that connected all towns of the Incan territory and led travelers up the steep mountains of Peru.
Through terrace farming, the process of farming on a hill or mountain by cutting out a flat surface, the Incas were able to provide crops such as potatoes, maize, and quinoa to its towns. The success of the Incan agricultural system was due in part to the system of canals that helped irrigate the crops on the terraces. The Incas’ system of farming grew, covering more than two million acres of Peru. It wasn’t until the invasion of the Spanish conquistadors that the agricultural practices began to decline. The Spanish forced the Incas to cultivate Spanish crops using the agricultural practices brought over from Spain.
The Incan population began to die as a result of the new demands of the Spanish, eventual war with the invading conquistadors, and exposure to European diseases. The agricultural practices of the Incas died along with the population.
Click on the link below and watch the slideshow to see how the farming practices of the Incas is being revived in the Andes Mountains today.
Based on the photos in the slideshow and the descriptions given, describe ways in which the Incas' farming practices can help today’s farmers of Peru.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The restoration of the canals can provide a more productive system of water usage and allow traditional methods of farming, such as terrace farming, to be used effectively.

The Incan Empire thrived until the arrival of Francisco Pizarro, a Spanish conquistador on his second exploration to South America in November 1533. Pizarro first executed Atahualpa, the last Incan emperor, and then thousands of other Incas. Pizarro took the gold, silver, and other riches of the Incas and sent them back to Spain. Next, Pizarro and Spanish reinforcements captured Cuzco, the capital of the Incan Empire. Finally, Pizarro named himself the Spanish governor of the entire Incan territory.

The Incas attempted to retaliate against the Spanish, but their efforts were quickly crushed. The Spanish then enslaved the Incas. It is still unclear what effectively ended the Incan civilization; it is believed that it is the combination of the Spanish conquest and exposure to European diseases such as smallpox.
Sources of images used for this section as they appear, top to bottom: