
Source: San _Andreas, Robert E. Wallace, U.S. geological Survey
A transform boundary is the zone between two plates sliding horizontally past each other. When two plates meet each other, they can cause folding and cracking of the rock. The transformation of the crust by folding or cracking occurs very slowly, often only a few centimeters or inches in a year. This occurrence causes what is commonly known as faults and they often produce earthquakes. Transform boundaries usually happen on the ocean floor, however, a few occur on land, for example the San Andreas Fault zone in California.
Scroll over the image below to identify the San Andreas Fault.
The image below is an aerial view of the San Andreas Fault. This part of the fault slices through the city of San Luis Obispo in California.

Source: San _Andreas, Robert E. Wallace, U.S. geological Survey
![]() Watch this video to learn more about the San Andreas Fault and its impact.
Watch this video to learn more about the San Andreas Fault and its impact.
Source: San Andreas Fault (Discovery Channel), NatureChannel7, YouTube
The graphic below shows how the San Andreas Fault Zone causes a shift between the Pacific Tectonic Plate and the North American Tectonic Plate. Movement in the San Andreas Fault Zone sometimes cause earthquakes in the area.
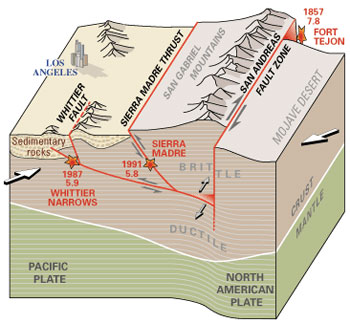
Source: San Andreas Fault Zone, U.S. Geological Survey

Source: City of Los Angeles, U.S. Geological Survey
Take a look at the San Andreas Fault line from above: ![]() Andreas Fault
Andreas Fault
![]() Watch the following video clips of various earthquakes in California.
Watch the following video clips of various earthquakes in California.
Source: Jan 9, 2010 Eureka, CA Earthquake, David Yancey, U.S. Geological Survey
Source: Earthquake in Los Angeles 1994, sailorclose, YouTube
Source: California Earthquake Captured- July 29, 2008, Badabuscuit, YouTube
Imagine that you live in Los Angeles, California, you have learned that a good friend is planning to move to the area, your friend has some concerns (your friend saw the video clips!) about the impact of the San Andreas Fault being so close. Write your friend a quick email that includes the following: