The purpose of the state constitution is to determine where the power and authority lie within the state’s government. The state constitution also provides basic freedoms for its citizens, while limiting the power of the government. These are elements of the U.S. Constitution that many state constitutions in the United States also include.
The Texas Constitution is similar to the U.S. Constitution for several reasons. First, both documents have a preamble, bill of rights, and articles that create three branches of government. Second, the idea of federalism exists in both constitutions, and third, both documents reflect similar constitutional principles.
![]() Click on each of the constitutional principles below to learn more.
Click on each of the constitutional principles below to learn more.
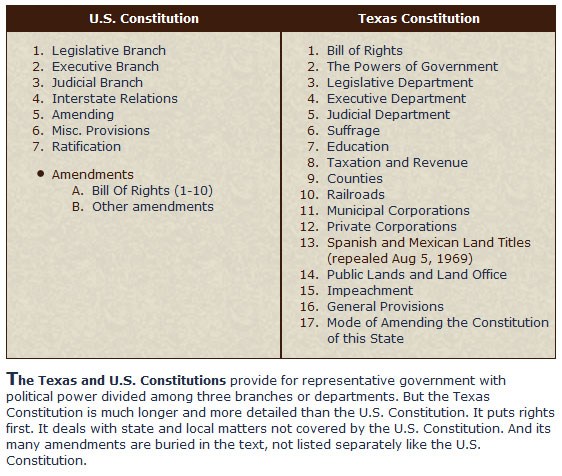
Analyze the above table to see a comparison between the two table of contents for the U.S. and Texas Constitutions, and then answer the following questions in your notes.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The Texas Constitution is longer and has more content than the U.S. Constitution.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Both documents have sections for the three branches of government and a bill of rights.
While the bill of rights in the Texas Constitution is located at the beginning of the document, the bill of rights in the U.S. Constitution is located in the end. The other difference between the Texas Constitution and the U.S. Constitution is the number of amendments. In the U.S. Constitution, there are only 27 amendments, including the bill of rights; the Texas Constitution has been amended nearly 400 times, and the amendments can be found throughout the document.
In this lesson, you will learn more about the constitutional principles of the Texas State Constitution and the ways in which the Texas Constitution and the U.S. Constitution are similar and different. This lesson will also examine ways in which the Texas Constitution has been revised throughout the history of Texas.