
Source: The History of Biology de Erik Nordenskiöld, Ed. Knopf, 1928 (domaine public), Wikimedia Commons
The study of genetics begins with an Austrian monk named Gregor Mendel. Mendel was born in 1822 in Heinzendorf, Austria. At the age of 18, Mendel went to study science and mathematics at the University of Vienna.

Source: The History of Biology de Erik Nordenskiöld, Ed. Knopf, 1928 (domaine public), Wikimedia Commons
When he was 21, Mendel joined the monastery in what is now Czechoslovakia. While at the monastery, Mendel was in charge of the garden. In this garden, Mendel would unlock the secrets of genetics and change biology forever.
Many biologists, researchers, and students have been curious as to why Mendel chose to use pea plants in his genetics research. There are several reasons why Mendel chose to work with pea plants.
First, pea plants grow and reproduce quickly. This helped Mendel study many generations over a short period of time. Second, pea plants are easily bred, and third, pea plants have a variety of characteristics, or traits. A trait is a specific characteristic, such as seed shape or flower color.
Mendel studied seven traits shown in the image below.
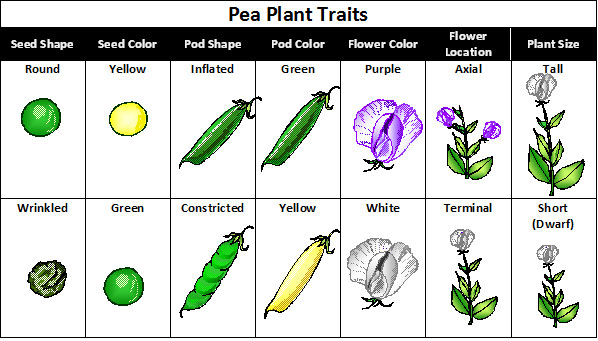
Source: Pea Plant Characteristics, Mariana Ruiz, Wikimedia Commons

Source: Self Pollination, Kids Encyclopedia Britannica
Pea plants are flowering plants and have both the male and female reproductive structure on the same plant. Pea plants are normally, self-pollinating, which means the pollen fertilizes the egg of the same flower. The image to the right shows what happens during self-pollination. Mendel’s pea plants were “true breeding,” meaning if the plants self-pollinated, the plants would always produce offspring with the same traits as the parents.

Source: Adapted From: Cross-Pollination, The University of Waikato
Mendel did not allow the plants in his garden to self-pollinate. Instead, he cross-pollinated the plants. The diagram to the left shows cross-pollination. By using cross-pollination, Mendel was able to control what traits were crossed.