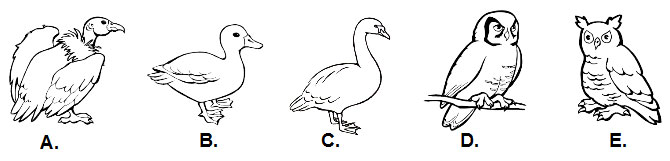
If you were asked to identify the following birds, you probably would have very little trouble identifying organisms A through C. You could probably identify that D and E are owls, but do you know the difference between the two species?

If there are over 10 million different species of plants and animals on Earth, how can organisms be identified? One answer to this question is “by using a dichotomous key.” A dichotomous key is a tool that allows the user to determine the identity of items in the natural world, such as trees, wildflowers, mammals, reptiles, rocks, and fish.
The word dichotomous means “divided into two parts.” Dichotomous keys are made up of a series of paired descriptive statements or questions with two responses. The user chooses the appropriate response, based on the characteristics of the unknown organisms. The user goes through the descriptive statements until the identity of the organism is determined.
![]() Watch the following video to learn more about dichotomous keys.
Watch the following video to learn more about dichotomous keys.
Source: Dichotmous Key Tutorial, Nicole Hall, YouTube
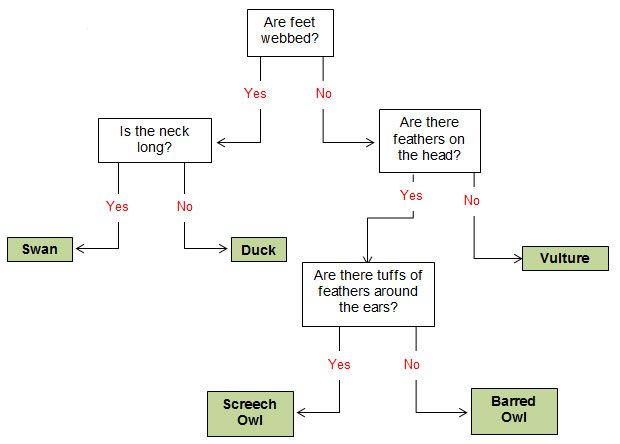
The dichotomous key below can be used to identify the birds pictured above. The dichotomous key is shown in both a table format and a branching diagram format.
| 1. | a. Feet are webbed. | Go to #2 |
| b. Feet are not webbed. | Go to #3 | |
| 2. | a. Neck is long. | Swan |
| b. Neck is not long. | Duck | |
| 3. | a. Feathers are on the head. | Go to #4 |
| b. No feathers on the head. | Vulture | |
| 4. | a. Tufts of feathers are around the ears. | Screech Owl |
| b. No tufts of feathers are around the ears. | Barred Owl |
![]() Let’s go through the dichotomous key and identify some of the birds pictured above. Follow these guidelines when using a dichotomous key.
Let’s go through the dichotomous key and identify some of the birds pictured above. Follow these guidelines when using a dichotomous key.
Sources for images used in the interactive, as they appear, top to bottom: