Organic compounds are compounds that contain at least one carbon atom chemically bonded to a hydrogen atom. There can be other atoms present in organic compounds, but there must be at least one carbon bonded to a hydrogen atom.
Biomolecules are organic compounds that are produced by living organisms.
Biomolecules are classified into one of four groups: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, or nucleic acids.
![]() Review basic information on the four groups of organic compounds. Click on each of the boxes below.
Review basic information on the four groups of organic compounds. Click on each of the boxes below.
Our bodies need carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals, and water to live. We need these nutrients in order for our cells to carry out life processes such as energy conversion, growth, and repair.
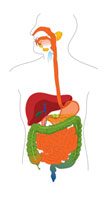
Source: Digestive System, Wikimedia Commons
The carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids that we eat are not in a usable form for our cells. The digestive system must break down these biomolecules into their simplest form in order to be used by our cells. Metabolism is the process that modifies molecules into other forms, so that the molecules can be used or stored by the body.
The breakdown of biomolecules into their simplest, usable form involves chemical changes. Anytime bonds between atoms are formed or broken, a chemical reaction takes place. Chemical reactions in the body would happen very slowly or not at all if it were not for the help of enzymes. Enzymes are molecules, produced by the body, that speed up chemical reactions. Enzymes are produced in the mouth, stomach, pancreas, and small intestine.