
Source: Pyramids at Giza and Coliseum at Dusk, Wikimedia Commons
Have you ever looked at pictures of the Egyptian pyramids or the Flavian Amphitheatre, also known as the Coliseum in Rome, Italy and wondered how they were built?

Source: Pyramids at Giza and Coliseum at Dusk, Wikimedia Commons
The first pyramid is thought to have been constructed between 2630 BC and 2611 BC, and construction on the Coliseum began in 70 AD and was completed in 80 AD. How did the ancient Egyptians and Romans build these massive structures without the use of modern technology? They used simple machines, such as pulleys and inclined planes to help them complete their work. A simple machine is a machine that changes a force’s direction or strength that makes work easier.
An inclined plane is a flat surface with one end raised higher than the other end. Inclined planes can be found all around us. The slides and ramps pictured below are examples of inclined planes.

Sources: Slide, Wikimedia Commons
Wheel Chair Ramp, Wheel Chair Assistance.com
Moving Truck Ramp, Moving insider.com
Work can be calculated by multiplying force required to move and object by the distance the object was moved. Work is measured in units called Joules (J.)
Work = Force × Distance
An inclined plane helps us do work by decreasing the force that we have to use to move an object through a vertical distance. There has to be a tradeoff, though; the smaller force has to be applied for a longer distance.
For example, if you lift a 20-N object a height of 5 meters, you have done 100 J of work. The inclined plane might only require us to apply a force of 10-N to move the same object to the same height, but we would have to apply that force a distance of 10 meters. We are still doing 100 J of work, but we are exerting a smaller force over a longer distance.
Remember, force is measured using a spring scale in units called Newtons (N).
In the following online lab, you will investigate how inclined planes change the amount of force needed to move an object. You will also calculate the amount of work completed.
Copy the data table onto your paper.
Mass of bag, marbles, and rubber band:________________________________
Distance (cm) |
Force (N) |
Work Completed (J) |
|
| Without Inclined Plane | |||
| With Inclined Plane |
![]() Click on the Next button to begin the online lab.
Click on the Next button to begin the online lab.
A pulley is a simple machine that uses a wheel and a chord to help you lift or lower objects. We use pulleys every day. The images below are examples of pulleys people use every day.

Sources: Fishing Pole, Amazon
US Flag, United States Flag.com
Pulley at top of flag pole, Flag Poles.com
Tow Truck, Amazon
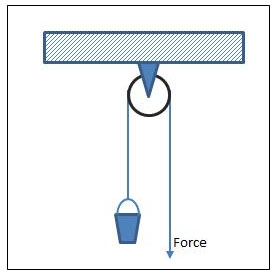
Source: Single Fixed Pulley, Meritnation
There are two types of pulleys, fixed pulleys and movable pulleys. A fixed pulley is a pulley that is attached, or fixed, to a surface such as a ceiling and stays in place as you use it. Fixed pulleys are best used for lifting objects that you cannot push upward because a fixed pulley changes the direction of the force you use to move an object. To lift an object with a fixed pulley, you first attach one end of the pulley cord to the object or load. Then you pull on the other end of the cord. When you pull on the cord, the wheel turns and changes the direction of your force. The amount of force you used to pull on the cord must be equal to or greater than the weight of the object. However, the pulley still makes it easier to lift the object because pulling down is easier than lifting an object up.
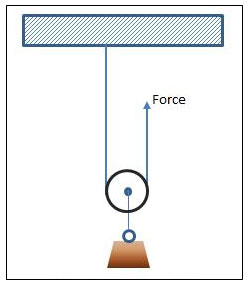
Source: Moveable Pulley, Meritnation
A movable pulley moves with the object. Movable pulleys don’t change the direction of the force like fixed pulleys. Instead, movable pulleys change the amount of force needed to lift the object. Movable pulleys are best for lifting objects that are below you. In a movable pulley, the cord is threaded under the pulley’s wheel, and one end of the cord is attached to something that will not move. The object is attached to the hook at the bottom of the pulley. When you pull on the free end of the cord, both the wheel and the object move upward.
In the following online lab, you will explore how movable pulleys make work easier by changing the amount of force needed to lift an object. You will also calculate the amount of work completed.
Copy the data table onto your paper.
Mass of bag, marbles, and rubber band:________________________________
Distance (cm) |
Force (N) |
Work Completed (J) |
|
| Without Pulley | |||
| With Pulley |
![]() Click on the Next button to begin the online lab.
Click on the Next button to begin the online lab.