- Observe the elements at room temperature.
- Note if the element is a solid, liquid or gas.

Some properties of matter can be easily observed by using senses; these are called physical properties. Other properties are not as easily observed. Chemical properties are properties of matter that require altering the substance before they can be observed. Properties of matter can be used to identify elements as metals, nonmetals and metalloids.
In this lesson, you will use physical properties to classify elements as metals, nonmetals and metalloids. State of matter, luster, conductivity, and malleability are the physical properties you will use to classify the elements.
The descriptions below describe physical properties of matter. Read each description and then brainstorm how you could safely test each property. Note your ideas using your own paper.
Whether an element is a solid, liquid or gas at room temperature indicates if the element is a metal, nonmetal or metalloid.
Brainstorm and describe a procedure to test this property.

Matter that can be pounded or rolled into flat sheets without shattering is said to be malleable. Matter that shatters and breaks into pieces when pounded is brittle.
Brainstorm and describe a procedure to test this property.

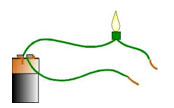
Electricity must have a closed path before it can travel from a battery through a light and then back. Matter that allows electricity to flow through it easily is called a conductor. Insulators do not allow the electricity to pass through easily.
Brainstorm and describe a procedure to test this property.


The way matter reflects light from its surface is called luster. Matter that reflects a large amount of light is called shiny. Matter with a dull luster reflects little light from its surface.
Brainstorm and describe a procedure to test this property.

Sources for images used in this section, as they appear, top to bottom: