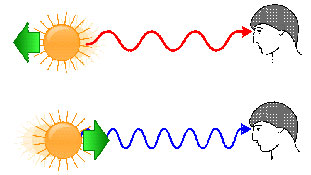
Source: Redshift Blueshift, Bender235, Wikimedia Commons
When astronomers analyze the light that comes from distant stars and galaxies, they can tell a lot about their motion because of the Doppler effect. Every element within a star has a specific pattern of light frequencies that it emits as the star shines. When looking at distant galaxies, astronomers observe the expected pattern for an element, but every frequency slightly shifts toward the red side of the spectrum. The light is experiencing a Doppler shift because the galaxy is moving away from the Earth.

Source: Redshift Blueshift, Bender235, Wikimedia Commons
![]() Watch the following video showing how the Doppler effect impacts light, and then answer the questions that follow.
Watch the following video showing how the Doppler effect impacts light, and then answer the questions that follow.
Source: The Doppler Effect, BYUIS, YouTube
What is happening to the behavior of the wavelengths of light as the object is moving away?

What is happening to the behavior of the wavelengths of light as the object is moving toward us?

This is the primary evidence that scientists use to theorize that the universe is expanding.
You've investigated how the Doppler effect is seen in light and sound. Now let's investigate how that looks in other applications using both light and sound.