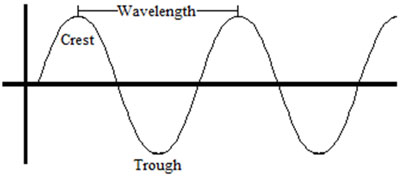
Adapted from: transverse, Mr. Clintberg's Studyphysics
If the medium vibrates perpendicular to the direction that the energy is moving, the wave is called transverse. The maximum positive displacement is called a crest, and the maximum negative displacement is called a trough.

Adapted from: transverse, Mr. Clintberg's Studyphysics
Common examples of transverse waves are waves on a string and light waves.
 Radio Tower |
 Microwave |
 X-ray |
When you think of microwaves, radios, and x-rays, you may not think about transverse waves, but each of these everyday objects works because of transverse waves. They are a part of the group of transverse waves known as electromagnetic waves. Look at the image below and answer the following questions.
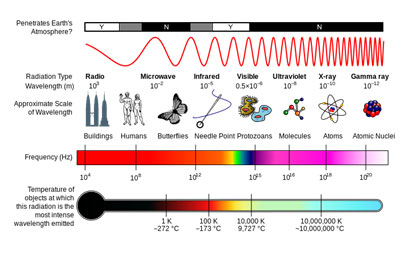
Source: Electromagnetic Spectrum, NASA, Wikimedia Commons
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The wavelengths of an X-ray are close together, very small (atomic size).
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Microwaves have wavelengths that are further apart and are much larger than X-ray waves.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Different wave characteristics allow the waves to travel differently through different types of media (like the example of the Earth’s atmosphere on the chart above). Also, the different wave characteristics allow them to interact with different temperatures.
Now that you have looked more deeply at the characteristics and behaviors of transverse waves, in the next section you look at longitudinal waves.
Sources for images used in this section, as they appear, from top to bottom: