 Source: Linear Heat Flow, Tooto, Wikimedia Commons
Source: Linear Heat Flow, Tooto, Wikimedia Commons
Heat is thermal energy transferred from one system or object to another. Heat energy is transferred in three ways: conduction, convection, and radiation. We often confuse heat with temperature. Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic activity of the particles of a substance.
Heat transfer is the movement of thermal energy from one object to another. When an object absorbs heat, its particles gain kinetic energy and they vibrate or move faster (remember—kinetic energy is energy of motion.)
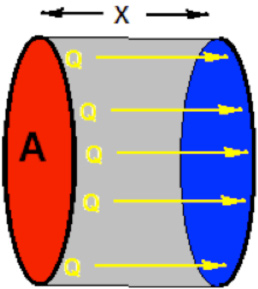
As shown in the following image, heat ALWAYS flows from a warmer area to a cooler area.
 Source: Linear Heat Flow, Tooto, Wikimedia Commons
Source: Linear Heat Flow, Tooto, Wikimedia Commons
Conduction is heat transfer by direct contact. The higher energy atoms of a warm object directly vibrate the lower energy atoms of a cooler object. If I step on a warm sidewalk with no shoes, the warmer sidewalk transfers thermal energy to my cooler feet. Conduction is also how heat can transfer from one part of a material to another. Conduction requires a medium to transfer heat.

![]() Watch the following video to see heat being transferred from one end of a metal rod to the other through conduction.
Watch the following video to see heat being transferred from one end of a metal rod to the other through conduction.
Source: Heat transfer by conduction demonstration, Mshopland, TeacherTube
How do we know that the heat was moving along the metal rod?
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required. The wax holding the push-pins in place was melted by the heat as it moved along the rod.