In this final section, you will take a brief look at how pressure impacts kinetic and potential energy in atoms and molecules. Pressure related to molecular kinetic theory takes into consideration increases and decreases in pressure. The table below notes some of the changes.
| Increasing pressure on a substance | Decreasing pressure on a substance |
|
|
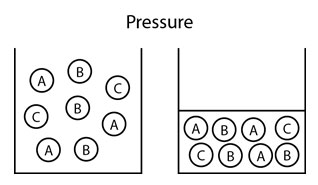
An example of one effect of pressure change can be seen in the image below. It shows the impact of increased pressure on kinetic energy of molecules. Increased pressure inhibits molecular movement, possibly altering the state from a liquid to a solid.

Now let’s take a moment to watch a demonstration of pressure changes impacting different types of substances. In the video, the investigators change the pressure on different types of everyday molecules including water, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide.
![]() As you watch the video, consider the following question:
As you watch the video, consider the following question:
How is the kinetic and potential energy of the atoms changing?
Source: Solid Nitrogen, Vacuum Cooling and Dry Ice, 1veritasium, You Tube


Remember the "friction welding" video from the beginning of the module? After learning about kinetic and potential energy in atoms and the various related properties, how would you describe the following concepts as seen in the video?
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
As the machine begins to work, the kinetic energy from the machine is transferred to the substance being welded. This increase in energy raises the potential energy of the electrons in the atoms. The atoms as heat and light release this potential energy as they "fall" back down to the previous shell.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The temperature of the metal substance is raised as kinetic energy from the friction is added to the molecules of the substance being welded.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
As the machine is rotating, the friction between the heat and pressure alters the metal substance briefly turning it into a liquid state to make the weld. The metal substance then goes back to a solid state as the heat and pressure are reduced.