Equation: PEs = one half 1 2 kx2

Try these practice problems. If you need to, click on the hint button. When you're done, click on the check your answer link to see the final answer.
A spring-loaded dart gun contains a spring with k = 10 numerator: N, denominator: m N m . When fully inserted, the 0.002 kg dart compresses the spring 0.05 m. How much energy is stored in the spring?


After the dart is released, all the energy becomes kinetic energy. What is the speed of the dart after it is released? Friction and air resistance are negligible.

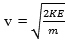
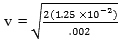

Assume the same gun is fired straight up. If all of the energy becomes gravitational potential energy, how high will the dart go?


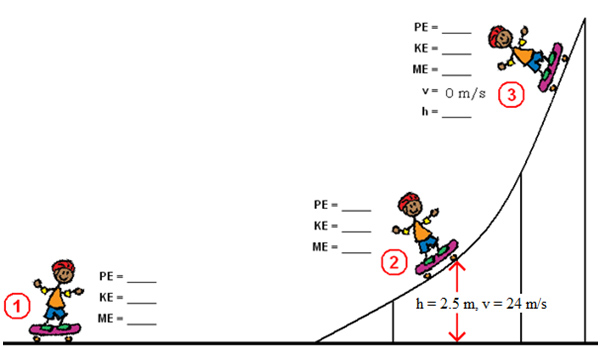
Adapted from: image 051, Energy files, Mr. Fizix
Use the illustration provided to answer the next three problems. The height is 0 m at point 1. Friction is negligible.
Determine the potential energy PE, the kinetic energy KE, and the total energy ME at point 1.


Determine the potential energy PE, the kinetic energy KE, the mechanical energy ME at point 2.


Determine the potential energy PE, the kinetic energy KE, and the height h at point 3.