
In the previous sections, you studied what power is and tried a few sample calculations. In this section, you will look at how power is related to series and parallel circuits.

![]() The following simulation allows you to build your own circuit and measure the current and voltage. Build the circuits shown, and answer the questions after each one.
The following simulation allows you to build your own circuit and measure the current and voltage. Build the circuits shown, and answer the questions after each one.
In the Tools box, click on Voltmeter and click on Non-Contact Ammeter. Construct the series circuit shown in the figure below. (Your circuit does not have to look exactly like the figure below, but should be similar.)
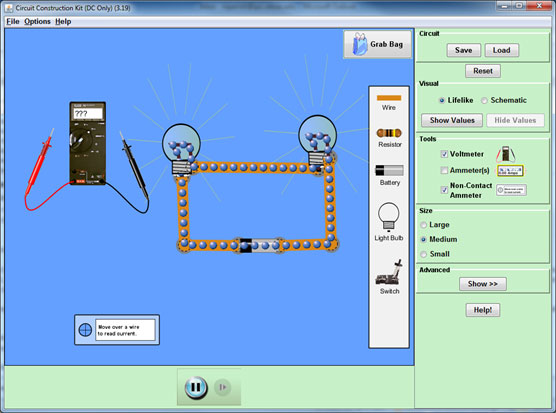
Source: Circuit construction kit dc, The University of Colorado – physics
Click play to start the animation. To measure a voltage, use your mouse to place the red and black probes from the voltmeter on either side of an object in the circuit. To measure current, drag the ammeter so that the crosshairs are over a wire.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
I = 0.45 A
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
9 V
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
P = IV
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Each bulb has a voltage drop of 4.5 V.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
P = IV
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Battery: 4.05 W
In the Tools box, click on Voltmeter and click on Non-Contact Ammeter. Construct the parallel circuit shown in the figure below. (Your circuit does not have to look exactly like the figure below, but should be similar.)
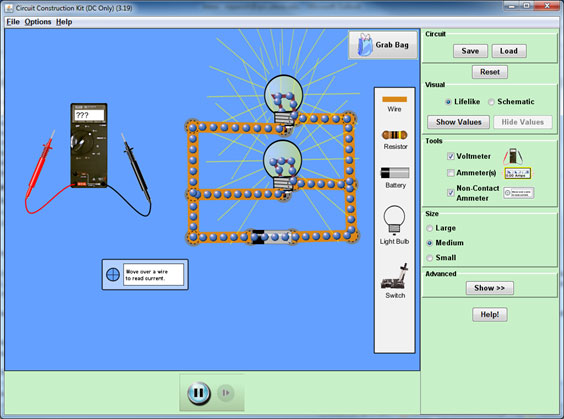
Source: Circuit construction kit dc, The University of Colorado – physics
Click play to start the animation. To measure a voltage, use your mouse to place the red and black probes from the voltmeter on either side of an object in the circuit. To measure current, drag the ammeter so that the crosshairs are over a wire.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Current through battery: 1.8 A
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
9 V
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
P = IV
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
9 V
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
P = IV
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
Battery: 16.2 W