Recall how Ohm's law can be used within a circuit to calculate current. The same equation is used to calculate the voltage drop across resistors in a circuit. It is called voltage drop because any circuit element that uses energy will show a decrease in electric potential.
Let’s practice calculating voltage by solving the problems below.
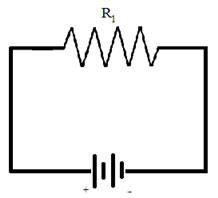
Calculate the potential difference (voltage drop) across the resistor in the following simple circuit if R1 = 10 Ω and the battery voltage = 3 V.



Calculate the potential difference (voltage drop) across each of the three resistors in the following circuit if R1 = 1.0Ω, R2 = 2.0Ω, and R3 = 3.0Ω and the battery's voltage = 12 V.
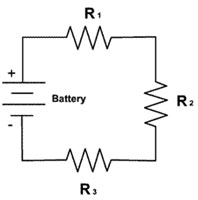 Source: DC circuits-series, school for champions
Source: DC circuits-series, school for champions 



| R1 = 1Ω V = IR V = (2.0 A)(1.0Ω) V = 2.0 V |
R2 = 2Ω V = IR V = (2.0 A)(2.0Ω) V = 4.0 V |
R3 = 3Ω V = IR V = (2.0 A)(3.0Ω) V = 6.0 V |


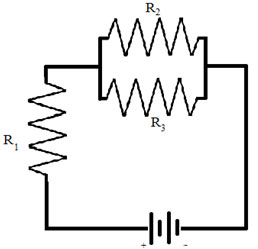
Calculate the potential difference (voltage drop) across each of the three resistors in the following circuit if
R1 = 1.0Ω, R2 = 2.0Ω, and R3 = 3.0Ω and the battery's voltage = 12 V.
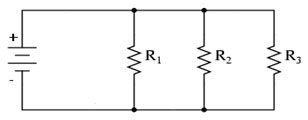 Source: DC circuits Parallel, School for Champions
Source: DC circuits Parallel, School for Champions 



Calculate the potential difference (voltage drop) across each of the three resistors in the following circuit if
R1 = 1.0Ω, R2 = 6.0Ω, and R3 = 3.0Ω and the battery's voltage = 9 V.