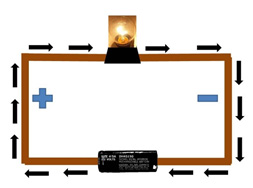

The job of a battery in a circuit is to convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy, which causes charge to flow through the circuit. Then, this energy is used to do specific tasks by the elements in a circuit. Each of the tasks performed by the circuit, whether it is simple like generating light or complex like storing information or making decisions within a digital chip, uses up some of that energy.

Source: Voltmeter, Northerntool
In order to know exactly how much energy there is in a circuit, it is important to first know how much charge there is. However, this can be difficult. Instead of measuring the energy itself, scientists use a voltmeter to measure the electric potential of a point in the circuit. The voltmeter measures how much energy one coulomb of charge would have at that point in a circuit.
Any two parts of a circuit that are directly connected by a wire have the same electric potential. Any two parts of a circuit that are separated by a battery or by a circuit element with any resistance would have different electric potentials. This allows us to measure the potential difference, or voltage, between any two points in a circuit.
![]() Watch the following video to view examples of electrical potential difference.
Watch the following video to view examples of electrical potential difference.
Source: Electric Potential Difference, John Rodgers, YouTube