Electric circuits allow us to harness and use the electric force for a variety of uses. The simplest circuits use the
voltage from a battery or generator to push electrons through a conductor. The movement of these electrons
is called an electric current. The electrons move through different parts of the circuit to make everything from light
bulbs to computers work.
![]() The following video shows an introduction to what circuits are and how they work.
The following video shows an introduction to what circuits are and how they work.
Source: Circuits (part1), Khan Academy, YouTube
![]() Visit The Simple Circuit & Ohm's Law, to see an animation that models a simple circuit. The fundamental equation that governs electric circuits is Ohm's Law. The equation is written:
Visit The Simple Circuit & Ohm's Law, to see an animation that models a simple circuit. The fundamental equation that governs electric circuits is Ohm's Law. The equation is written:

![]()
Source: Ohm's Law, The University of Colorado – Physics
In the simulation above, use the sliders to change the voltage and resistance and see how the current in the circuit changes.
What happens to the current when you make the voltage larger?
What happens to the current when you make the resistance smaller?
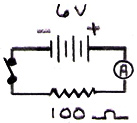
A 6 V battery is connected to a 100 Ω resistor in a simple circuit. What is the value of the current measured by the ammeter in the circuit?