Source: Nuvola di elettroni, ARTE, Wikimedia
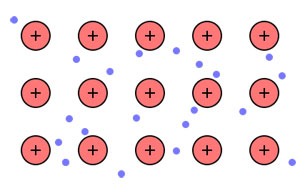
Materials that present very low resistance to the flow of electricity are known as conductors. These materials conduct electricity well because of the way that the atoms bond with each other. Look at this model of the bonding structure of many metals.

Source: Nuvola di elettroni, ARTE, Wikimedia
Notice that the nuclei (shown with plus signs) are in a rigid structure, but some of the electrons are spread out and can move freely around the metal. These free electrons interact strongly with light that strikes the surface of a conductor, making it appear shiny. In addition, the free electrons in conductors help them to conduct heat well, and also endow the material with ductility, which is the ability to bend or be deformed without breaking. Thus, the fact that electrons are free to roam in a conductor leads to a whole host of physical properties that can be used to identify conductors. The best example of a good electrical conductor is any metal.
Solutions that contain a lot of ions (like salt water) are also very good conductors. The ions in solutions act like the free electrons in metals.