Think about nuclear stability as trying to balance a really tall object. If it has a wide base, it will be easy to balance. If it has a wide base, it will be easy to balance; if it has a narrow base, it will be harder to balance.

Others, however, are very unstable and will fall over very easily.
Helium is the most stable of all the elements with more than one particle in its nucleus. This is because it contains two protons and two neutrons. The fact that there are four particles in the nucleus means that each of the four can touch all three of the others. This puts them close together and makes the strong force very effective.
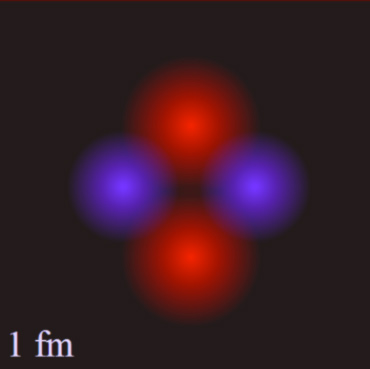
Source: Helium Nucleus, DZadventiste, Wikimedia Commons
There are three ways that a nucleus can become unstable.
When a nucleus is unstable, it is only a matter of time before it undergoes a process called decay. Nuclear decay is the natural process by which the nucleus tries to make itself stable.
There are three kinds of decay:
Alpha (α) |
Beta (β) |
Gamma (γ) |
| Generally involves a nucleus that is too big | Generally involves a nucleus with the wrong number of protons | Generally involves a nucleus with too much energy |