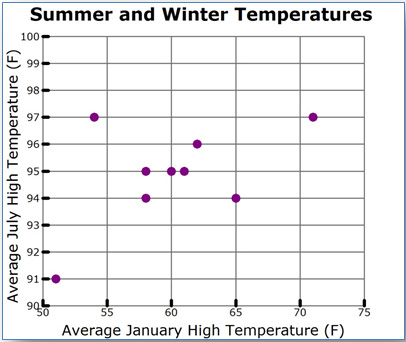
A scatterplot is a graph that is used to compare two different data sets.
City |
Average January |
Average July |
College Station |
61 |
95 |
Austin |
62 |
96 |
Longview |
58 |
94 |
Wichita Falls |
54 |
97 |
Victoria |
65 |
94 |
McAllen |
71 |
97 |
San Angelo |
60 |
95 |
El Paso |
58 |
95 |
Amarillo |
51 |
91 |
A scatterplot is created by rewriting the table values as a set of ordered pairs, and plotting one variable along the x-axis and one variable along the y-axis.


Scatterplots are typically used to determine if there is a relationship between the two variables being represented in the scatterplot. Researchers, engineers, and statisticians frequently use scatterplots to look for these relationships since they are a visual representation. In a scatterplot, you may spot trends that you don't easily see in a data table.
There are three major types of relationships that you will analyze.
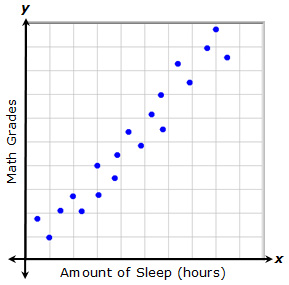
A relationship with a positive trend is one in which both variables increase at the same time. In this example, each point represents the amount of sleep that a student had and the grade that they received on a recent math quiz. As the amount of sleep increases, the math grade increases.
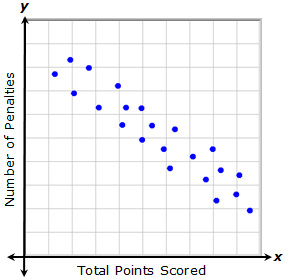
A relationship with a negative trend is one in which as one variable increases, the other variable decreases. In this example, each point represents the total points that a player scored and the number of penalties they received during a recent game. As the number of penalties increases, the total points scored decreases. Likewise, as the total points scored increases, the number of penalties received decreases.
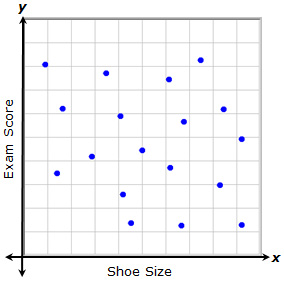
Sometimes, a relationship shows no trend. In this case, there is no detectable pattern in the data that allows you to say that as one variable changes, the second variable changes in a particular way. In this example, each point represents a student's shoe size and his or her recent social studies exam score. There does not appear to be a relationship between the shoe size and the exam score.