

Randomization is one important way to make sure that survey data can be used to reach valid conclusions.
Another factor that may influence the conclusions reached by survey data is bias. A survey has bias if the survey data has a tendency to overestimate or underestimate a particular characteristic that is being surveyed. In other words, the results of the survey are tilted toward one particular viewpoint.
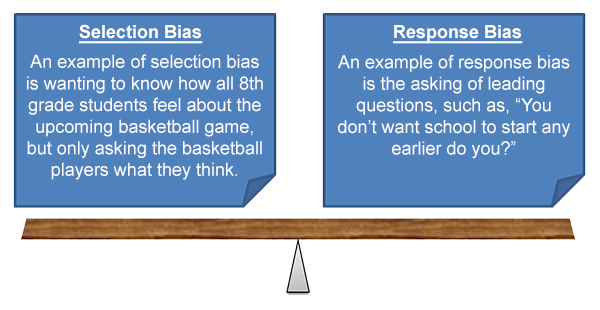
Bias can result from a variety of sources. One type of bias, selection bias, results from the selection of a sample that is not representative of the population being described.
Another type of bias, response bias, can come from the way that a survey instrument itself is constructed.
Sort the examples of bias below into two types of bias: selection bias and response bias.
For the following questions, determine if the sample is representative of the population or not.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The sample is not representative. The population is the people that live in the neighborhood, but the sample is only people who are riding an existing bus.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The sample is representative. The population is all students in Margie’s school, and the sample is a randomly selected portion of all students in the school.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The sample is not representative. The population is the people that live in Ruben’s city, but the sample is only people who are boarding an airplane to Las Vegas.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The sample is not representative. The population is all students at Robertson Middle School, but the sample is only students in Aleshia’s English class.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
35% of 440 students, or 154 students