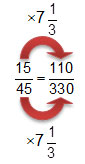You compared two different types of probability: theoretical probability and experimental probability.
Theoretical probability is the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the number of total possible outcomes. Experimental probability is the ratio of the number of times an event occurs to the total number of trials.
In other words, theoretical probability is a ratio that describes what should happen, but experimental probability is a ratio that describes what actually happened.
Differences between Theoretical and Experimental Probabilities
You can use theoretical and experimental probabilities to distinguish between the likelihood of something happening from a purely theoretical perspective and the chances of something happening based on actual results.
|
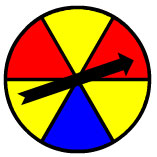
Arturo's Results
|
|
Color
|
Number of Spins
|
|
Red
|
9
|
|
Yellow
|
16
|
|
Blue
|
5
|
|
Arturo's Experimental Probability Compared to the Theoretical Probability
|
|
Color
|
Theoretical Probability |
Experimental Probability |
|
Red
|
2 over 6
2
6
|
9 over 30
9
30
|
|
Yellow
|
|
16 over 30
16
30
|
|
Blue
|
1 over 6
1
6
|
5 over 30
5
30
|
Making Predictions
You can also use theoretical and experimental probabilities to make predictions from situations by treating them like proportion problems.
The results of a random survey of 8th grade students at Jamison Middle School showed that 15 out of 45 students like eating lunch at 10:30 a.m. If there are 330 students in the 8th grade at Jamison Middle School, approximately how many students would be expected to prefer eating lunch at 10:30 a.m.?
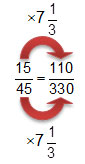
110 students would like eating lunch at 10:30 a.m.