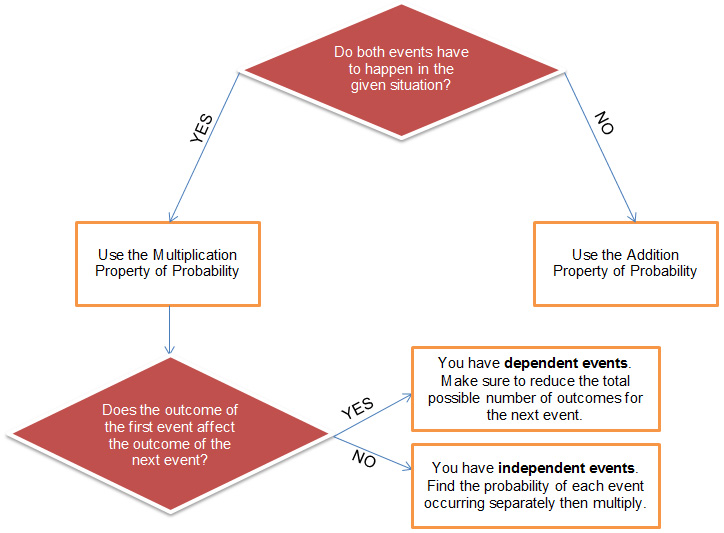
In this lesson, you investigated different ways to compute the probability of two or more events occurring.
Mutually exclusive events are two or more events that cannot both happen at the same time. You can calculate the probability of a set of mutually exclusive events by using the Addition Rule of Probability as follows:
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)
Independent events are two or more events that occur in sequence where the outcome of the first event does not affect the outcome of the events that follow. You can calculate the probability of a series of independent events by using the Multiplication Rule of Probability as follows:
P(A and B) = P(A) × P(B)
Dependent events are two or more events that occur in sequence where the outcome of the first event does affect the outcome of the events that follow. You can calculate the probability of a series of dependent events by using the Multiplication Rule of Probability as follows:
P(A and B) = P(A) × P(B|A)
The flowchart shown can be used to help you determine how to approach different probability problems.
