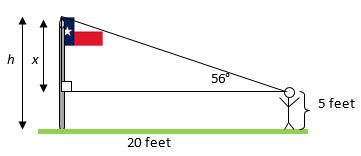
Finding the Height of the Flagpole.
In this section, real world problems are solved using Trigonometric Functions. A calculator is needed.
The ancient Greeks studied right triangles in great detail. They noticed that for a set of similar right triangles (right triangles with side lengths that are proportional and corresponding angles congruent), the ratios of the side lengths had practical applications that allowed them to solve problems, especially with regard to art, architecture, and measuring distances. Greece has a lot of mountains and deep valleys, and directly measuring distances from one place to another is often difficult or even impossible. Trigonometry made it possible to measure those distances.
There are many different units that scientists and mathematicians use to measure angles, including degrees, radians, and gradients. It is very important that your calculator be set to “DEGREES” mode before solving problems involving trigonometric ratios.
Finding the Height of the Flagpole.

Fill in the blanks.
![]() Move your mouse over the blanks to reveal the answers.
Move your mouse over the blanks to reveal the answers.
Step 1: Identify the Reference Angle, the Adjacent Leg, the Opposite Leg, and the Hypotenuse.
Identify them in your diagram by mousing over the image below of a triangle.
Find: the Reference Angle, Adjacent Leg, Opposite Leg, and the Hypotenuse
Step 2: Identify the information you are given and the information you are looking for.
Step 3: Identify the trigonometric ratio that relates the two side lengths from Step 2.

Step 4: Set up a ratio, including the angle measure, known side length, and unknown side length.

Step 5: Solve.

Step 6: The value you found in Step 5 is the height of the flagpole above the observer’s eye. Add back the height of the observer to find the full height of the flagpole, h.
A palm tree that is 15 yards tall casts a shadow along the beach that is 50 feet long. What is the angle of elevation of the sun above the ground? Round to the nearest degree
Note: Angle of elevation: An angle that is measured above a particular reference point (usually a line of sight).
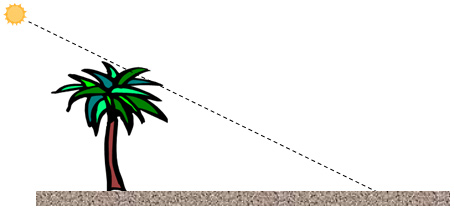
Step 1: Identify the reference angle, the adjacent leg, the opposite leg, and the hypotenuse. Label them in your diagram by dragging your mouse over the appropriate label to the appropriate side of the triangle.
![]()
Step 2: Identify the information you are given and the information you are looking for.
Step 3: Identify the trigonometric ratio that relates the two side lengths from Step 2.

Step 4: Set up a ratio, including the angle measure, known side length, and unknown side length.

Step 5: Solve.

A forest ranger stand is 200 feet above the ground. A fire is spotted in the distance. The angle of depression from the ranger stand to the fire is of 5°. About how far is the fire from the base of the tower? Round to the nearest foot
Note: Angle of depression: An angle that is measured below a particular reference point (usually a line of sight).

Step 1: Identify the reference angle, the adjacent leg, the opposite leg, and the hypotenuse. Identify them in your diagram by mousing over the appropriate label to the appropriate side of the triangle.
Find: x feet, 5°, Adjacent Leg, Opposite Leg, 200 feet, and Hypotenuse:
![]()
Step 2: Identify the information you are given and the information you are looking for.

Step 3: Identify the trigonometric ratio that relates the two side lengths from Step 2.

Step 4: Set up a ratio, including the angle measure, known side length, and unknown side length.

Step 5: Solve.