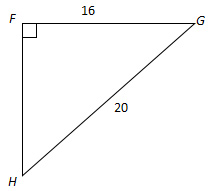
Given: Right triangle FGH with right angle F, FG = 16 and GH = 20. Find m ∠ H.
This section uses the trigonometric ratios to find angles of right triangles. A calculator is needed.
Trigonometric ratios are used to calculate the measures of one (or both) of the acute angles in a right triangle, if you know the lengths of two sides of the triangle.
Given: Right triangle FGH with right angle F, FG = 16 and GH = 20. Find m ∠ H.

![]() Move your mouse over the blanks to reveal the answers.
Move your mouse over the blanks to reveal the answers.
Step 1: Identify the reference angle, the adjacent leg, the opposite leg, and the hypotenuse.
Identify them in your diagram by mousing over the image below of a triangle.
Find: Adjacent Leg, Opposite Leg, Hypotenuse, and Reference Angle.
Step 2: Identify the information you are given and the information you are looking for.
Step 3: Identify the trigonometric ratio that relates the two side lengths from Step 2.

Step 4: Set up a ratio, including the angle measure, known side length, and unknown side length.
Step 5: Solve for the angle measure using the inverse trigonometric ratio. On your calculator, this can be found using the 2nd-SIN or INV-SIN keystroke. Round the answer to the appropriate place value.