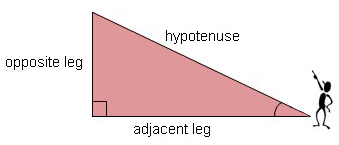
This section defines the trigonometric ratios sine, cosine and tangent.
In a right triangle, there are two legs and a hypotenuse. In order to distinguish between two legs, we need a reference point. Mathematicians use one of the two acute angles as the reference point and call it the reference angle. With respect to the reference angle, one leg is the adjacent leg, or the leg right next to the reference angle; and the other leg is the opposite leg, or the leg on the opposite side of the triangle.

If two triangles are similar, the ratios of corresponding sides are equal.
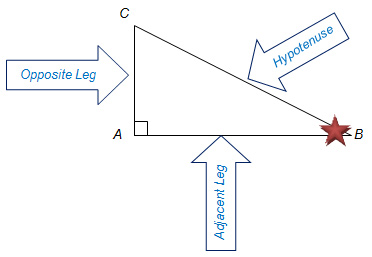
Each of these three ratios has a special name.
Consider right triangle ABC
Trigonometric Ratio |
Abbreviation |
Ratio of Side Lengths |
Example |
Sine |
sin |
sin A = Opposite Leg Hypotenuse |
sin B = AC BC 
|
Cosine |
cos |
cos A = Adjacent Leg Hypotenuse |
cos B = AB BC 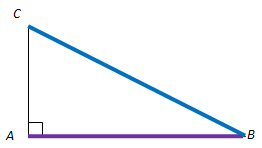
|
Tangent |
tan |
tan A = Opposite Leg Adjacent Leg |
tan A = AC AB 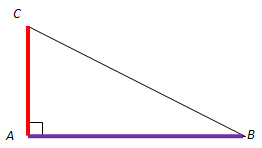
|