 GJH and m
GJH and m
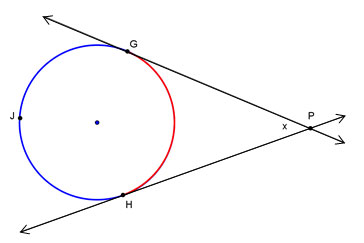
 GH relate to the angle measure represented by x?
GH relate to the angle measure represented by x?Another type of relationship you will explore with circles is that of arcs and angles formed by intersecting tangents.
Once again, brainstorm a possible hypothesis to help you guide your thinking. Use what you already know about the relationship between arcs and angles found inside and outside of a circle.
In your notes, write out a prediction in response to the following question:
How will m
 GJH and m
GJH and m
 GH relate to the angle measure represented by x?
GH relate to the angle measure represented by x?
Using the Intersecting Tangents applet linked below, manipulate the endpoints of
 ADB so that you always have the red and blue arcs in opposite places on the circle. To change the size of your circle, click and drag point A or point E. Observe the changes in m∠C as you change the arc measurements.
ADB so that you always have the red and blue arcs in opposite places on the circle. To change the size of your circle, click and drag point A or point E. Observe the changes in m∠C as you change the arc measurements.

![]() Click on the image below to open the applet. Manipulate the angle so that m
Click on the image below to open the applet. Manipulate the angle so that m
 ADB is 240 degrees, then 220 degrees, and finally 200 degrees.
ADB is 240 degrees, then 220 degrees, and finally 200 degrees.
Copy the table below into your notes. Then use the measures of the arcs to complete the table and answer the questions below.
| m ∠C | m
 ADB ADB |
m
 AB AB |
m
 ADB – m ADB – m
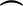 AB AB |
| 240° | |||
| 220° | |||
| 200° |
 ADB – m
ADB – m
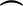 AB?
AB?
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
m ∠C = 1 over 2 1 2 (m ADB – m
ADB – m
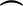 AB)
AB)

 ADB and
ADB and
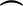 AB are the intercepted arcs of the two tangents, what can you say about the measure of the angle between two intersecting tangents and the measures of the intercepted arcs?
AB are the intercepted arcs of the two tangents, what can you say about the measure of the angle between two intersecting tangents and the measures of the intercepted arcs?
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
If two tangents intersect at a common point, then the measure of the angle formed is equal to half the difference of the measures of the intercepted arcs.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The two intercepted arcs together create the whole circle. One arc is always a major arc with measure greater than 180°. The other arc is always a minor arc with measure less than 180°.
How does the relationship that you discovered for two intersecting tangents compare to the relationship you discovered for two secants that intersect outside a circle?
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The relationships are very similar in that the measure of the angle of the intersection is equal to one-half the difference of the measures of the intercepted arcs.
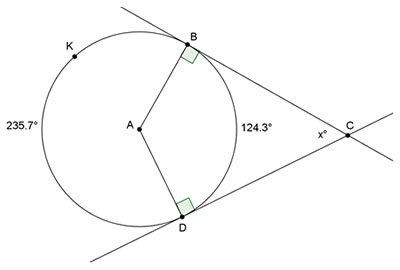
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The measure of the angle between two tangents from a common point is one-half the difference of the measures of the intercepted arcs.
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
m∠BCD = 1 over 2 1 2 (m BKD – m
BKD – m
 BD)
BD)
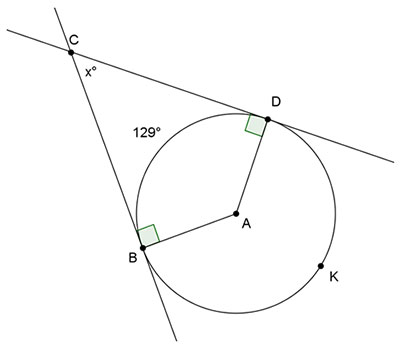
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The measure of the angle between two tangents from a common point is one-half the difference of the measures of the intercepted arcs. Also, the sum of the measures of the two intercepted arcs is 360°.