![]() Watch this short video showing sulfuric acid applied to fabric.
Watch this short video showing sulfuric acid applied to fabric.
Source: Corrosive Property of Sulfuric Acid, Basco36, YouTube

Source: Cloud, Boy Face, Women, Cartoon balloon, OCAL, Clker
Remember, an Arrhenius acid will dissociate hydrogen ions (H+) in solution. For example, an acid such as HCl will disassociate into H+ and Cl- ions as shown in the equation below.
HCl → H+ + Cl-
An Arrhenius base will dissociate hydroxide (OH-) ions in solution. For example, a base such as NaOH will dissociate into Na+ and OH- ions as shown in the equation below.
NaOH → Na+ + OH-
The strength of an acid or a base is determined by how easily it dissociates hydrogen or hydroxide ions in solution. In other words,
The strength of acids and bases are defined by using the pH scale, which ranges from 1 to 14, and is a logarithmic scale. Acids cause tissue damage by denaturing proteins. Ions, specifically an increase in the hydrogen ion concentration, [H+], can kill and/or stimulate nerve endings causing the sensation of pain.
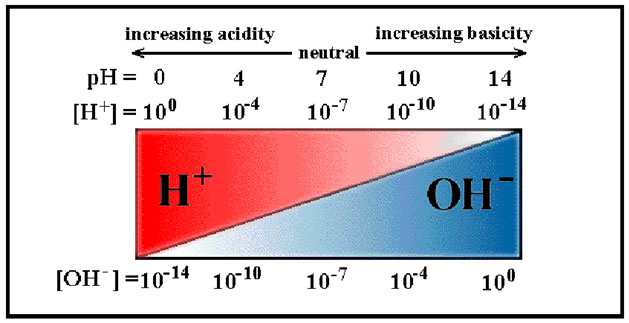
Source: pH scale, UTDallas
As you can see in the pH scale above, a smaller pH value indicates high concentrations of H+ ions. A larger pH value indicates high concentration of hydroxide (OH-) ion and a high potential to bond H+.