Source: Acid in Water, Hyperphysics
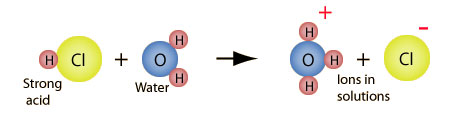
When a molecule of hydrochloric acid, HCl, is added to water, a proton (H+) is attracted to the negative pole (the oxygen) of a water molecule. The proton sticks to the water molecule, forming a hydronium ion, or H3O+. The image below illustrates this process.

Source: Acid in Water, Hyperphysics
The chemical equation for this process is shown below.
HCl + H2O → H3O + Cl
If you put this process into words, the word reaction would be as follows.
Acid + Water → Hydronium ion + Anion
Sometimes this reaction is simplified as HCl → H+ + Cl-. This is the simplest type of acid, called an Arrhenius acid.
Acids are compounds that dissociate (give off) hydrogen ions (protons) when dissolved in water. Acids have a pH value lower than 7. The word acid is derived from the Latin word "acere" which means sour. All acids have a sour taste. They also turn blue litmus paper red. Acids also react with active metals. Acids are electrolytes and will conduct electricity in solution.
![]() Watch the following video of different metals reacting with acids.
Watch the following video of different metals reacting with acids.
Source: Reactivitity of Metals with HCl - Qualitative Lab, MrGrodskiChemistry, YouTube
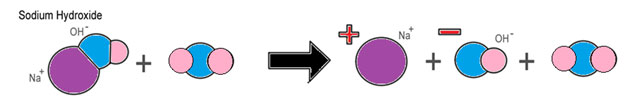
When a molecule of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is added to water, it dissociates into a hydroxide ion (OH-) and a metal ion. The image below illustrates this process.
Source: Bases, Biology Corner
The chemical equation for this process is shown below.
NaOH + H2O → Na+ + OH- + H2O
If you put this process into words, the word reaction would be as follows.
Base + Water → Metal + Hydroxide ion + Water
Bases are compounds that dissociate hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water. Bases have a pH value higher than 7, typically with a bitter taste, and turn red litmus paper blue. When bases are applied to a surface, they often make that surface feel slippery, like soap. Bases are also electrolytes, and will conduct electricity in solution.