![]() Watch the following video where the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid allows you to easily visualize relationships between reagents and products, as well as limiting reagents.
Watch the following video where the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid allows you to easily visualize relationships between reagents and products, as well as limiting reagents.
Source: Limiting Reactants, Jim Holler, YouTube
![]() Watch the following video for a refresher on how to use stoichiometry to identify the limiting reagent when you are given information for multiple reagents.
Watch the following video for a refresher on how to use stoichiometry to identify the limiting reagent when you are given information for multiple reagents.
Source: Part 3 Limiting and Excess Reactants, John Michael Hammond, YouTube
Let’s try solving the following problems. Do as much work as you can before clicking on the answer buttons to check your work. If you get stuck, try to figure out where you got lost in the problem.
In the synthesis reaction below, 40.0 grams of iron are reacted with 30.0 grams of oxygen.
4 Fe + 3 O2 → 2 Fe2O3
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
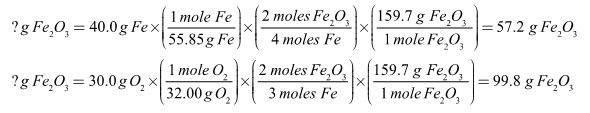

Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The fraction of iron(III) oxide produced must equal the fraction of excess reagent used. Another way of saying this is that if all 30.0 grams of oxygen had reacted, 99.8 grams of iron(III) oxide would have been made. Since only 57.2 grams of iron(III) oxide were made, only 17.2 grams of oxygen actually reacted. The two variables, amount of reagent used and the amount of product made, are directly proportional to each other.

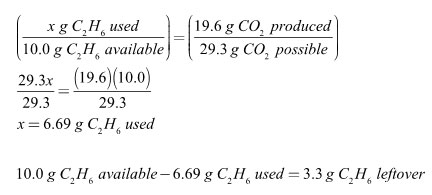
In the combustion reaction below, 10.0 grams of ethane, C2H6, are reacted with 25.0 grams of oxygen.
2 C2H6 + 7 O2 → 4 CO2 + 6 H2O
Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
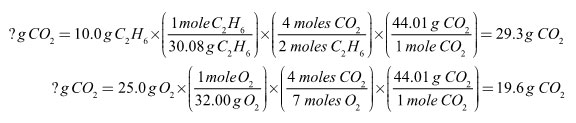

Interactive popup. Assistance may be required.
The fraction of carbon dioxide produced must equal the fraction of excess reagent used. Another way of saying this is that if all 10.0 grams of ethane had combusted, 29.3 grams of carbon dioxide would have been made. Since only 19.6 grams of carbon dioxide were made, only 6.69 grams of ethane were combusted. The two variables, amount of reagent used and amount of product made, are directly proportional to each other.