

The pea plant traits that Mendel studied were controlled by a single gene and therefore called monogenic traits. Many traits are produced by the interaction of several genes. Traits controlled by two or more genes are said to be polygenic traits. Many human traits such as height, skin color, hair color, etc. are results of polygenic traits.
The image below shows the varying scale of human skin color. Scientists believe that at least three different genes code for skin color. The allele for dark skin, D, is dominant over the allele for light skin, d. The variety of skin color seen in the human population depends upon how many dark-skin alleles are present.
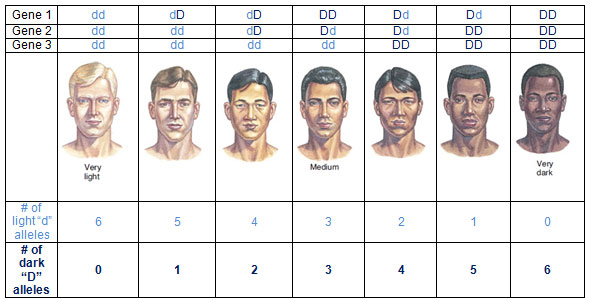
Source: Adapted From: Polygenic inheritance, McGraw Hill Education

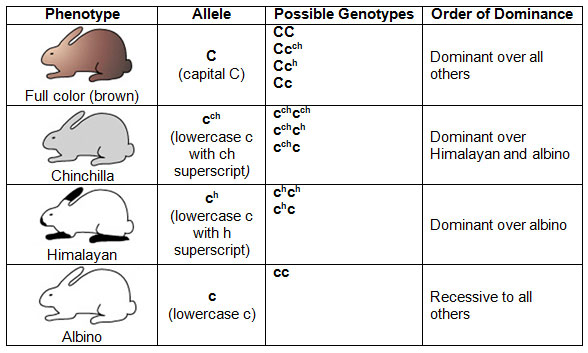
Source: Rabbit Fur Color Variety, Bumble Bee Acres
In the pea plants that Mendel studied, there were only two alleles for each trait, one dominant and one recessive. For example, the pea plant flower color was either purple or white. In multiple allele inheritance, there are more than two alleles for a particular trait. This is different from polygenic traits because in multiple allele inheritance, a single gene controls the trait where more than one gene controls the polygenic traits.
One of the best-known examples of multiple allele inheritance is coat color in rabbits. A single gene that has at least four different alleles determines a rabbit’s coat color. The four known alleles display a pattern of simple dominance that can produce four coat colors.
The chart below shows the phenotypes, possible genotypes, and order of dominance in rabbit color.
![]() Watch the following video to learn more about multiple allele inheritance in rabbit coat color, and see how offspring are predicted using Punnett squares.
Watch the following video to learn more about multiple allele inheritance in rabbit coat color, and see how offspring are predicted using Punnett squares.
Source: Chapter 11 Part 11- Multiple Alleles, MrDBioCFC, YouTube
Many other genes have multiple alleles including the human genes for blood type.