A gene is essentially a sentence made up of the bases A, T, G, and C that describes how to make a protein. Any changes to those instructions can alter the gene's meaning and change the protein that is made, or how or when a cell makes that protein.
Gene mutations that involve changes in one or a few nucleotides are called point mutations because they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence. There are three types of point mutations.
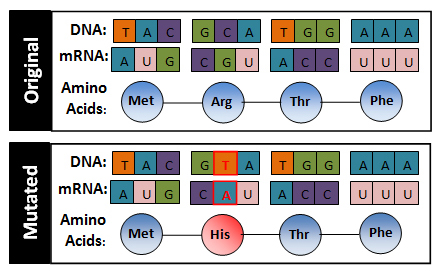
In a substitution mutations, one base is changed to a different base. Substitutions usually affect no more than a single amino acid and sometimes they have no effect at all. A substitution mutation is equivalent to changing one letter in a sentence, such as this example, where we change the 'c' in cat to an 'h':
| Original | The fat Cat ate the wee rat. | Substitution | The fat hat ate the wee rat. |

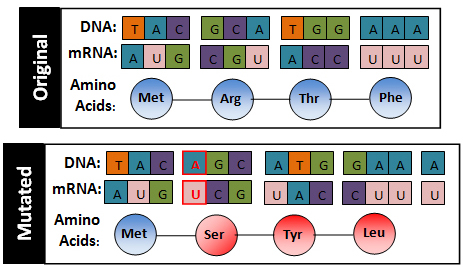
Mutations that result in the addition of extra DNA are called insertion mutation.
| Original | The fat cat ate the wee rat. | Insertion | The fat cat aat eth ewe era t. |
Mutations that result in missing DNA are called deletion mutation. In this example, the deletion eliminated the letter c.
| Original | The fat cat ate the wee rat. | Insertion | The fat ata tet hew eer at. |
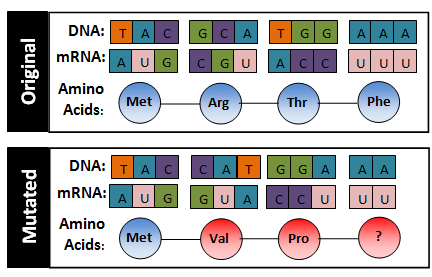
Insertions and deletions are also called frameshift mutation. Because our cells read DNA in three letter "words," adding or removing one letter changes each subsequent word. This type of mutation can make the DNA meaningless and often results in a shortened protein.
See if you can identify each of these changes in DNA and explain its effect on an organism.
| Second Base | |||||||
| U | C | A | G | ||||
 |
U | Phenylalanine | Serine | Tyrosine | Cysteine | U |  |
| Phenylalanine | Serine | Tyrosine | Cysteine | C | |||
| Leucine | Serine | Stop | Stop | A | |||
| Leucine | Serine | Stop | Tryptophan | G | |||
| C | Leucine | Proline | Histidine | Arginine | U | ||
| Leucine | Proline | Histidine | Arginine | C | |||
| Leucine | Proline | Glutamine | Arginine | A | |||
| Leucine | Proline | Glutamine | Arginine | G | |||
| A | Isoleucine | Threonine | Asparagine | Serine | U | ||
| Isoleucine | Threonine | Asparagine | Serine | C | |||
| Isoleucine | Threonine | Lysine | Arginine | A | |||
| Methionine | Threonine | Lysine | Arginine | G | |||
| G | Valine | Alanine | Aspartic Acid | Glycine | U | ||
| Valine | Alanine | Aspartic Acid | Glycine | C | |||
| Valine | Alanine | Glutamic Acid | Glycine | A | |||
| Valine | Alanine | Glutamic Acid | Glycine | G | |||
![]()