Source: Cell Differentiation in Multicellular Organisms, Sichuan University

Source: Cell Differentiation in Multicellular Organisms, Sichuan University
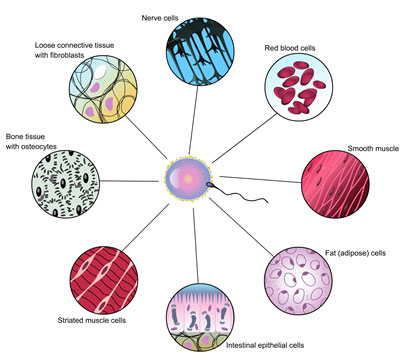
Living organisms can be made of a single cell, such as bacteria and protists, or they can be multicellular like plants, animals, and fungi. Unicellular organisms, like bacteria, are able to perform all life functions within one single cell. They can transport molecules, metabolize nutrients, and reproduce within this one cell. Organisms made of more than one cell need many different types of cells to carry out the same life processes. Each of these special types of cells has a different structure that helps it perform a specific function. Humans have many different types of cells with different jobs, such as blood cells that carry oxygen and nerve cells that transmit signals to all parts of the body. Cell differentiation is the process by which cells become specialized in order to perform different functions.
Even multicellular organisms begin as just a single cell. Getting from one single cell to billions of specialized cells that perform different functions is a process that happens with the regulation of DNA and RNA. It can also be influenced by factors in the environment.