There are two main benefits of glycolysis. First, glycolysis can produce ATP quickly and secondly, it does not require oxygen.
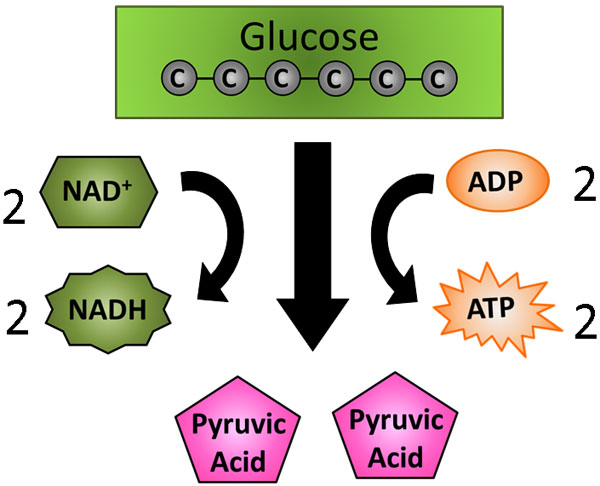
Remember that glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration and it takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Two ATP molecules are required and 4 are made. So during glycolysis there is a net gain of 2 ATPs. Also during glycolysis 2 NAD+ molecules are transformed in to NADH.
The diagram below represents what happens during glycolysis.

When cells generate large amounts of ATP through the process of glycolysis they quickly run into a problem. Within a short amount of time, all of the cell's available NAD+ molecules are filled with electrons. Without oxygen, the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain will not run, so there is nowhere for the NADH molecules to deposit their electrons.
![]() Watch the following animation to see what happens when you run out of oxygen.
Watch the following animation to see what happens when you run out of oxygen.
Without NAD+, the cell cannot keep going through glycolysis, and ATP production stops. When oxygen is not present, glycolysis is followed by a process called fermentation.
During fermentation, cells convert NADH back into the election carrier NAD+. This allows glycolysis to produce a steady supply of ATP.
As with glycolysis, fermentation also takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. There are two slightly different forms of fermentation - alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation.