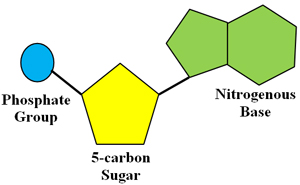

Nucleic acids are biomolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorous. Nucleic acids are polymers made from individual monomers called nucleotides. Nucleotides consist of three parts: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
The image below shows a more detailed structure of a nucleotide on the left. What makes each nucleotide different is the nitrogen-containing base that is attached to the phosphate group and sugar. The different nitrogenous bases are shown in the image on the left.
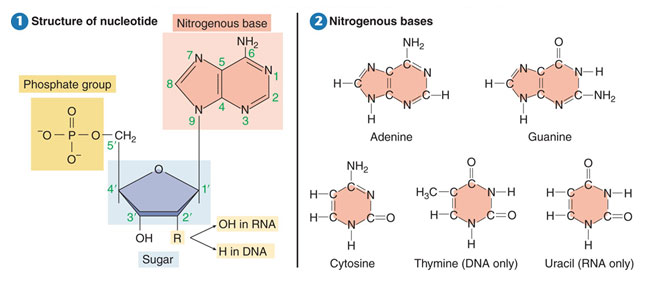
Source: Structure of nucleotide and nitrogenous bases, Yellow Tang
There are two main kinds of nucleic acids: ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
DNA is responsible for the long-term storage of information. DNA contains the instructions needed to construct other components of cells, such as proteins and RNA molecules.
The following are three types of RNA:
All three types of RNA help assemble proteins during protein synthesis.
2. What are the parts of a nucelotide?

3. What are the elements found in nucleic acids?

4. What are the functions of nucleic acids?