- y = 1
- x = 7

At times, you may be given a partial ordered pair and an equation, and you will be asked to determine the value of the missing variable.
Example: Let's say that you were told that (x, 6) is a solution to the equation 2x + 5y = 32 and you need to determine the value of x.
Algebraically, you would just need to substitute 6 for y in the equation and solve for x.
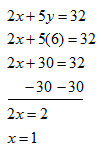
Example: If (−1, y) is a solution to the equation 2x – 7y = 40, what is value of y
This time, you would need to substitute -1 for x in the equation and solve for y.
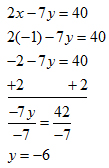
You could also enter the equation (in y = form) into your graphing calculator and look at the table of values that is generated by the equation.
For example, if we look at the equation for the last example (2x – 7y = 40) and rewrite it so that it is in y = form, the equation would be fraction; numerator: 2, denominator: 7 2 7 x – fraction; numerator: 40, denominator: 7 40 7 .
Enter this into your graphing calculator under Y1 and look at the TABLE for the y-value when x = -1.
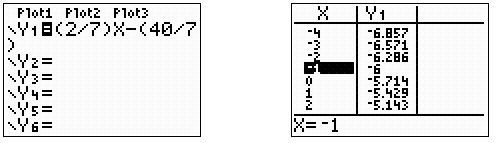
By looking at the table, we can see that when x = -1, y = -6.
Answer the following questions on your own paper.
