Many experimental procedures for the preparation of solutions call for stirring the solvent while adding the solute. Which of the following is always an effect of this procedure?
A. It decreases the solubility of the solute.
Incorrect. Stirring or agitation speeds the dissolving rate by increasing the amount of collisions between particles.
B. It brings the solute and solvent rapidly into contact.
Correct!
C. It decreases the reactivity of the solute.
Incorrect. Stirring or agitation speeds the dissolving rate by increasing the amount of collisions between particles.
D. It produces a double replacement reaction.
Incorrect. Stirring or agitation speeds the dissolving rate by increasing the amount of collisions between particles.
Hexane is a nonpolar solvent, while water is a polar solvent.
|
Solute |
Water |
Hexane |
|
C10H8, naphthalene |
Insoluble |
Soluble |
|
NH4Cl, ammonium chloride |
Soluble |
Insoluble |
|
CO(NH2)2, urea |
Soluble |
Insoluble |
|
C2H5OH, ethanol |
Soluble |
Soluble |
Which of the above examples demonstrates a nonpolar solute in a polar solvent?
A. CO(NH2)2 in hexane
Incorrect. Polar substances dissolve in polar solvents. If the substance is soluble in water, it is polar.
B. C2H5OH in hexane
Incorrect. Polar substances dissolve in polar solvents. If the substance is soluble in water, it is polar.
C. NH4Cl in water
Incorrect. Polar substances dissolve in polar solvents. If the substance is soluble in water, it is polar.
D. C10H8 in water
Correct!
How many moles of HNO3are needed to make 4.0 liters of a 2.5 M solution of HNO3?
A. 2.5
Incorrect. Molarity = moles/Liters.
B. 10
Correct!
C. 5
Incorrect. Molarity = moles/Liters.
D. 20
Incorrect. Molarity = moles/Liters.
A chemical engineer wants to react 500g of marble (CaCO3) with excess hydrochloric acid. In which of the following forms will the marble react most rapidly?
A. A solid sphere
Incorrect. Smaller particles have a larger surface area and react faster.
B. Fine powder
Correct!
C. Small chips
Incorrect. Smaller particles have a larger surface area and react faster.
D. A solid cube
Incorrect. Smaller particles have a larger surface area and react faster.
A chemist prepared a solution by heating 100 milliliters of water while adding KCl crystals until the crystals would not dissolve. He then sealed the clear solution and set it aside. After a few hours he saw that the solution had become cloudy and some solid had settled to the bottom of the beaker. Which statement best describes what happened?
A. Water molecules, trapped with the KCL crystals, were released after heating.
Incorrect. As the temperature of a solution decreases, the solubility of the solute decreases.
B. At lower temperatures, the solubility of the KCL decreased and recrystallization occurred.
Correct!
C. As the solution cooled, evaporation of water increased the KCl concentration beyond its solubility.
Incorrect. Lowering the temperature does not cause water to evaporate.
D. At increased temperatures, the solubility of KCl increased and remained too high after cooling.
Incorrect. As the temperature of a solution decreases, the solubility of the solute decreases.
A solution that contains more solute than it can dissolve at a given temperature is –
A. dissociated
Incorrect. Dissociation is a process in which ionic compounds separate into smaller charged particles.
B. saturated
Incorrect. Saturated solutions have exactly the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve.
C. supersaturated
Correct!
D. unsaturated
Incorrect. An unsaturated solution can dissolve more solute without changing any conditions.

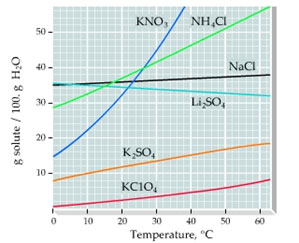
Which solute responds the most to temperature change?
A. K2SO4
Incorrect. Find the curve with the steepest slope.
B. NaCl
Incorrect. Find the curve with the steepest slope.
C. KClO4
Incorrect. Find the curve with the steepest slope.
D. KNO3
Correct!
The graph below shows the solubilities of various salts in 100 grams of water at a range of temperatures.

What mass of NH4Cl is needed to form a saturated solution if the NH4Cl is dissolved in 100 g of water at 48°C?
A. 30.0 g
Incorrect. Find the Y intercept at 48°C.
B. 56.0 g
Incorrect. Find the Y intercept at 48°C.
C. 40.0 g
Incorrect. Find the Y intercept at 48°C.
D. 50.0 g
Correct!
Which statement best describes why water dissolves most salts?
A. Water is polar, and salts form ions in solution.
Correct! Ionic compounds contain charged particles and dissolve in polar solutions like water.
B. Water has a different density than salts.
Incorrect. Ionic compounds contain charged particles and dissolve in polar solutions like water.
C. Water is nonpolar, and salts form ions in solution.
Incorrect. Ionic compounds contain charged particles and dissolve in polar solutions like water.
D. Water has the same density as salts.
Incorrect. Ionic compounds contain charged particles and dissolve in polar solutions like water.
The compound NaOH is classified as an Arrhenius base because, when the molecule dissolves in water, there is an increase in the concentration of –
A. hydrogen ions
Incorrect. Arrhenius bases dissociate OH- ions in solution.
B. sodium ions
Incorrect. Arrhenius bases dissociate OH- ions in solution.
C. hydroxide ions
Correct!
D. oxide ions
Incorrect. Arrhenius bases dissociate OH- ions in solution.
A sample of water has a pH of 6 at 25°C. What is the hydroxide concentration in this water sample?
A. 1 × 10-6 M
Incorrect. [H+]= 1 × 10-pH
B. 6 × 10-8 M
Incorrect. [H+]= 1 × 10-pH
C. 1 × 10-8 M
Correct! [H+]= 1 × 10-pH
D. 6 × 10-6 M
Incorrect. [H+]= 1 × 10-pH
Which substance can be classified as either an acid or a base according to the Bronsted-Lowry definition?
A. NH41+
Incorrect. This compound would only lose a H+ and be considered an acid.
B. HOH
Correct! Water can accept a H+ and be considered a base, or lose a H+ and be considered an acid.
C. H3O1+
Incorrect. This compound would only lose a H+ and be considered an acid.
D. HCl
Incorrect. This compound would only lose a H+ and be considered an acid.
Which of the following is a redox reaction?
A. 2H2O(l) → 2H2(g) + O2(g)
Correct! Hydrogen and oxygen have a change in oxidation state.
B. CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Incorrect. No change in oxidation state has occurred.
C. NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Incorrect. This is an acid-base reaction.
D. 2NH4Cl(s) + Ca(OH)2(s) → 2NH3(g) + 2H2O(l) + CaCl2(s)
Incorrect. No change in oxidation state has occurred.
What is the pH of a solution of NaOH with a hydroxide concentration of [OH] = 1 × 10-4 M?
A. -10
Incorrect. H+= KW/[OH-], pH= -log[H+]
B. -4
Incorrect. H+= KW/[OH-], pH= -log[H+]
C. 4
Incorrect. H+= KW/[OH-], pH= -log[H+]
D. 10
Correct!
Compared to a weak acid, a strong acid will —
A. form more quickly with a weak base
Incorrect. An acid is considered strong or weak based on its dissociation.
B. form more slowly with a weak base
Incorrect. An acid is considered strong or weak based on its dissociation.
C. dissociate less than 95 percent of its ions
Incorrect. A strong acid will dissociate 100 percent of its ions.
D. dissociate 100 percent of its ions
Correct!
The diagram below illustrates an apparatus used to test the conductivity of various solutions, and the table shows the degree of dissociation of some common acids.
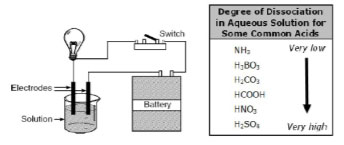
The stronger an acid or base is, the better it conducts electricity.
Which of the following would make the bulb glow most brightly?
A. NH3
Incorrect. NH3 has a very low degree of dissociation.
B. H2CO3
Incorrect. H2CO3 has a low degree of dissociation.
C. HNO3
Incorrect. HNO3 does
not have the highest degree of disassociation of the answer choices.
D. H2SO4
Correct!
Which of the following chemical reactions is correctly labeled?
A. 2KBr(aq) + Pb(NO3)2 →2KNO3(aq) + PbBr2(s), neutralization
Incorrect. This is a precipitate reaction because a solid product is formed.
B. MgCl2(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → Mg(OH)2(s) + CaCl2(aq), acid-base
Incorrect. This is a precipitate reaction because a solid product is formed. There is no acid present in the reactants.
C. 3CaCl2(aq) + K3PO4(aq) → Ca3(PO4)2(s) + 6KCl(aq), precipitation
Correct! A solid is formed.
D. NaHCO3(s) + NaOH(aq) → Na2CO3(aq) + H2O(l), oxidation-reduction
Incorrect. There is not a change in oxidation state.
Consider the reaction shown below.
NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq)àNaNO3(aq) + AgCl(s)
This reaction can accurately be classified as a(n) –
A. acid base reaction
Incorrect. Neither reactant is an acid or a base.
B. precipitation reaction
Correct! A solid is formed from two aqueous reactants.
C. combustion reaction
Incorrect. Oxygen is not a reactant and water is not formed.
D. oxidation reduction reaction
Incorrect. There is no change in oxidation state.
Three 10g samples of sugar are represented below.
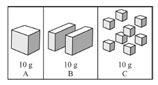
Which sample would dissolve the fastest in 100mL of water at 30oC?
A. A
Incorrect. Smaller particles have a larger surface area and react faster.
B. B
Incorrect. Smaller particles have a larger surface area and react faster.
C. C
Correct!
D. They all will dissolve at the same rate.
Incorrect. Smaller particles have a larger surface area and react faster.
A pharmacist needs to mix 20g of crystals of compound A and 10g of crystals of compound B. The mixture is then placed in 120mL of water to make cough syrup.
Which set of conditions will cause the compounds to dissolve the fastest?
A.
|
Size of Crystals (mm) |
Temperature (°C) |
Stirring (Y/N)? |
|
0.01-0.02 |
22.3 |
N |
B.
|
Size of Crystals (mm) |
Temperature (°C) |
Stirring (Y/N)? |
|
0.1-0.2 |
49.9 |
N |
C.
|
Size of Crystals (mm) |
Temperature (°C) |
Stirring (Y/N)? |
|
0.1-0.2 |
22.3 |
Y |
D.
|
Size of Crystals (mm) |
Temperature (°C) |
Stirring (Y/N)? |
|
0.01-0.02 |
49.9 |
Y |
Which of the following solutions has the highest concentration of solute?
A. 1.0 mol solute in 200mL of solvent
Correct!
B. 2.0 mol solute in 250 mL of solvent
Incorrect. Concentration is measured with Molarity (M=mol of solute/L of solution).
C. 3 mol of solute in 1L of solvent
Incorrect. Concentration is measured with Molarity (M=mol of solute/L of solution).
D. 4 mol of solute in 1.5L of solvent
Incorrect. Concentration is measured with Molarity (M=mol of solute/L of solution).
A crystal of KCl is dissolved in water. Which of the following statements explains why the dissolved salt does not recrystallize?
A. K+ and Cl- ions lose their charges in water.
Incorrect. Ions will retain their charges in water.
B. Water molecules surround the K+ and Cl- ions.
Correct!
C. K+ and Cl- ions leave the solution through evaporation.
Incorrect. The ions will remain dissolved in water.
D. Water molecules chemically react with K+ and Cl- ions.
Incorrect. Water will simply dissolve the ions.
Which best explains why water dissolves most salts?
A. Water is polar, and salts break into ions in solution.
Correct!
B. Water is nonpolar, and salts break into ions in solution.
Incorrect. Water is a polar molecule.
C. Water has the same density as salts.
Incorrect. Density does not explain solubility.
D. Water has a different density than salts.
Incorrect. Density does not explain solubility.
Some chemistry students were testing the solubility of carbonate when combined with different metal ions. Based on their observations below, write a rule for the solubility of carbonate. Include appropriate group numbers or names.
Observations:
|
|
Na+ |
Ca2+ |
Li+ |
Mg2+ |
K+ |
|
CO32- Carbonate |
No reaction |
Precipitate formed |
No reaction |
Precipitate formed |
No reaction |
Based on these observations which rule is correct?
A. All carbonate compounds are soluble.
Incorrect. Group 2 compounds are insoluble.
B. All carbonate compounds are insoluble.
Incorrect. Group 1 compounds are soluble.
C. Carbonate compounds that contain group 1 metals are insoluble.
Incorrect. No precipitate is formed with group 1 compounds.
D. Carbonate compounds that contain group 1 metals are soluble.
Correct! Compounds that contain group 1 metals are always soluble and do not form precipitates.
In the diagram below, sodium carbonate is dropped into a test tube containing calcium chloride.
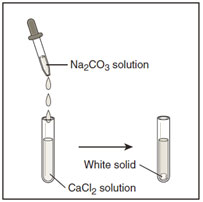
The white precipitate that formed is most likely –
A. NaCl
Incorrect. All group 1 compounds are soluble.
B. CaCO3
Correct!
C. Na2CO3
Incorrect. All group 1 compounds are soluble.
D. CaCl2
Incorrect. CaCl2 is a reactant in this reactant.
Which of the following effects is produced by the high surface tension of water?
A. Lakes don’t freeze solid in winter despite low temperatures.
Incorrect. Freezing is not related to surface tension.
B. A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond.
Correct!
C. Organisms resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions.
Incorrect. This is describing the high specific heat of water.
D. Water can act as a solvent.
Incorrect. Solvent ability is not the same as surface tension.
Which of the following compounds would have the highest conductivity value when put into solution?
A. NaCl
Incorrect. NaCl only dissociates into two ions.
B. MgF2
Incorrect. MgF2 only dissociates into 3 ions.
C. FeCl3
Correct!
D. Need more information
Incorrect. Count the number of ions in the formula.
Which of the following will form ions and conduct electricity when added to water?
I. NaOH
II. Al2O3
III. NH3
IV. CH3OH
A. I only
Incorrect. II will also dissociate into ions.
B. II only
Incorrect. I will also dissociate into ions.
C. I and II
Correct!
D. I, II, III, and IV
Incorrect. III and IV will not dissociate into ions.
Classify the following reaction:
HCl + NaOH→H2O + NaCl
A. Acid-base reaction
Correct!
B. Oxidation-reduction reaction
Incorrect. Water and an ionic compound are formed.
C. Precipitation reaction
Incorrect. Water and an ionic compound are formed.
D. None of the above
Incorrect. Water and an ionic compound are formed.